Preparation for the clients for following investigation
Subject: Gynecological Nursing

Overview
Most common reason to do a diagnostic laparoscopy is to look into pelvic pain or infertility. It can also be used to get rid of a cyst in the ovary or the tubes. The laparoscope is a medical tool with a bright light and a very small camera. In hysterosalpingography, 3 to 10ml of an opaque contrast medium are slowly injected through a catheter into the endocervical canal. This lets the uterus and fallopian tubes be seen on fluoroscopy and radiography.
It is a screening test that doesn't need a general anesthetic and can be done with a high degree of accuracy. The bimanual examination is an examination of the size and position of the uterus. The radio-opaque dye (usually water-soluble, rarely oil-based), 10-15 ml., is gently injected by attaching the loaded syringe to the cannula or Foley catheter. Mammography is an x-ray test that looks at breast tissue with a low dose of radiation. It is used to check for disease in women over 40, and it is recommended that they get one every year.
The American Cancer Society recommends that all women between the ages of 35 and 40 get a baseline mammogram. The Papanicolaou (Pap) smear or pap test is a screening procedure for cervical cancer. It tests the presence of precancerous or cancerous cells on the cervix. Women with an increased risk of breast cancer should have a mammogram annually after age 40. This test is safe during pregnancy for pregnant clients but the cytobrush cell retrieval tool is not recommended for the pregnant diet.
A breast examination may also be performed as part of the gynecologic evaluation. A colposcopy is a way to look closely at the cervix, vagina, and vulva to look for abnormal cells. A colposcope is a stereoscopic binocular microscope with low magnification. It is useful for finding a suspicious lesion, but a pathologist needs to look at the tissue to make a final diagnosis. When something is wrong during a pelvic exam, a cervical biopsy may be done.
It may also be done if a Pap test finds cells that don't look right. If you have an HPV infection and your HPV test comes back positive, you may also need a biopsy. The cervix is swabbed with 3% acetic acid to remove mucus and improve the contrast between tissue types. The vaginal speculum is inserted using water as a lubricant if a Pap smear is to be performed before the biopsy. Cervical samples are placed in specimen containers with formalin solution.
Fine needle aspiration (FNA) is a quick and simple procedure that removes fluid or cells from a breast lesion or cyst. If fluid is extracted, it is placed on a slide, while tissue is deposited in a sterile container. Under a microscope, a cytologist can also study frozen-section samples. Adhere to sterile technique and standard precautions. Adhere to a calm atmosphere during the procedure.
The older person may find it difficult to maintain positions when required to do so for lengthy periods. Advise the patient to use warm, moist compresses for pain and to wear a supportive bra. A high Vaginal Swab (HVS) is a technique used to obtain a sample of discharge from the vagina. This is then sent for culture and sensitivity. It is commonly used to test for the presence of candidiasis infection, bacterial vaginosis and trichomonas vaginalis.
Transvaginal ultrasound is an imaging scan used to look at a woman's reproductive organs, including the uterus, ovaries, and cervix. A vaginal speculum is inserted and the specimen is obtained by direct smear, aspiration, or saline lavage. The probe called a transducer is placed inside the vagina. The probe sends out sound waves, which reflect off body structures. A radiologist can see the picture on a TV monitor and move the probe around the area to see the pelvic organs.
Laparoscopy
Laparoscopy is a type of endoscopy that is minimally invasive. During this procedure, the doctor will use a thin surgical telescope with a small lens on one end to look inside the abdomen. The most common reason to do a diagnostic laparoscopy is to look into pelvic pain or infertility. Since this is a surgical procedure, it is usually done after other tests have failed to find the cause of the pain. It can also be used to get rid of a cyst in the ovary or the tubes.
Most of the time, a small cut is made near the belly button, and CO2 gas is pumped into the belly. This moves the abdomen away from the organs inside the body so that the surgeon can see them better. Two more small cuts may be made in the abdomen so that other tools, like a probe that moves organs, can be used during the surgery. At the end of the process, the gas is taken out. Through the trocar, the laparoscope, a medical tool with a bright light and a very small camera, is put into the abdomen. In the operating room, a TV screen shows a big picture of what the camera sees. Small cuts are made to put other instruments in. The surgeon moves these to do the surgery, whether it's to remove an organ, take a tissue sample, or fix an organ.
Indications
- Staging for ovarian malignancy
- Hosts for following an investigation
- Adnexal torsion
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Abnormal pelvic scan
- Subfertility
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (including TB)
- Unexplained pelvic mass
- Congenital pelvic abnormality
- Endometriosis
- Acute or chronic pelvic pain
Test Procedure
- Place the client in a supine position in the surgical setting and insert a Veres needle into the peritoneal cavity while the client has general or local anesthetic.
- A trocar and sheath is inserted into the cavity; the trocar is then removed for the insertion of the laparoscope.
- CO2 or nitrous oxide insufflates the peritoneum, creating a pneumoperitoneum.
- The laparoscope is advanced into the peritoneal cavity through a small periumbilical incision and the following is visualized: omentum, the surface of the liver peritoneum, gallbladder, portions of the spleen, diaphragm, a serosal surface of the small bowel and colon, and in females the ovaries, fallopian tube, and uterus.
- Areas of pathology are noted and biopsies may be obtained.
Nursing Intervention
Before Test
- Explain the test procedure and the purpose of the test.
- Assess the client's knowledge of the test.
- Instruct the client to be NPO for 6-8 hr prior to the procedure.
- The patient should be instructed to avoid taking natural products and medications with known anticoagulants, antiplatelets, and thrombolytics, or decrease the dose as ordered. The number of days to withhold medications is dependent on the type of anticoagulants.
During Test
- Adhere to standard precautions.
After Test
- If the client has had a general anesthetic, follow the standard protocol for care of the postoperative
- patient. Observe for any other listed complications.
- Restrict activity for 2-7 days. Inform the client that residual carbon dioxide effects may produce shoulder and abdominal pain for 1-2 days.
Contraindications
- Mechanical or paralytic bowel obstruction
- Generalized peritonitis Diaphragmatic hernia
- Major intraperitoneal hemorrhage (e.g. shock)
- Massive obesity
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Large abdominal mass advanced pregnancy
- Irreducible external hernia
- Multiple abdominal incisions
- Severe cardiorespiratory disease
Hysterosalpingography
In hysterosalpingography, 3 to 10 ml of an opaque contrast medium are slowly injected through a catheter into the endocervical canal. This lets the uterus and tubes be seen on fluoroscopy and radiography. If the fallopian tubes are open, the dye will rise up into the uterus and tubes, making them bigger, and then it will leak out into the peritoneal cavity. It can check both the uterine cavity and the fallopian tubes. It is a good screening test that doesn't need a general anesthetic and can be done with a high degree of accuracy. Before the procedure, it is recommended that chlamydia testing be done, preferably as part of the initial work-up of the female partner. Antibiotics should also be used to cover the procedure.
Indications
- To assess the feasibility of tuboplasty by studying the location and extent of tubal pathology.
- To study the patency of the fallopian tubes in infertility and postoperative tuboplasty.
- To study uterine anomalies such as the septate and cornuate uterus.
- To detect uterine synechiae.
- To detect uterine polyp
- To study the incompetence of internal OS.
Test Procedure
- It is done as an outpatient procedure, without any anesthesia, in the Department of Radiology. Premedication with atropine and analgesia may be required in an apprehensive woman to prevent tubal spasms.
- The woman is asked to empty her bladder.
- Place the woman in the lithotomy position, perineal area cleaned with betadine and draped. • The bimanual examination is done to note the size and position of the uterus.
- The cervix is exposed and held with an Allis forceps, Rubin's cannula, Leech Wilkinson cannul or Foley catheter No. 14 is introduced gently into the uterine cavity beyond the internal os (bulb of the catheter distended to prevent leakage). The cone of Rubin's cannula snugly fits into the external os.
- The radio-opaque dye (usually water-soluble, rarely oil-based), 10-15 ml., is gently injected by attaching the loaded syringe to the cannula or Foley catheter.
- The uterine cavity and fallopian tubes are visualized as the dye passes through them during fluoroscopy.
- At a specific time desired, X-rays are taken for a permanent record. The instruments are withdrawn, and the woman is observed for half an hour.
Patient Preparation
Before Test
- Explain the test procedure and the purpose of the test.
- Assess the client's knowledge of the test.
- Assess for potential allergies to contrast medium.
- Inform the client that during injection of contrast medium, a burning sensation may be felt for a few seconds behind the eyes or in the jaw, teeth, tongue, or lips.
- Assess for anxiety and provide sedation as ordered. Administer preoperative medication 30 min before the procedure.
- Obtain baseline vital signs and perform a neurological assessment.
During Test
- Provide privacy.
- Adhere to standard precautions.
- Assess for allergic reactions to the contrast medium.
After Test
- Assess the client for possible abdominal discomfort or nausea immediately following the study
Contraindications
- Previous history of allergy to iodine, eggs, or shellfish. Infections of the vagina or fallopian tubes.
- Uterine bleeding
- Ferential Touth
Nursing Considerations
Pregnancy:
- Radiation and IV contrast should be avoided in pregnant women if possible.
- Wear the protective lead shielding to protect the fetus if it is determined this test is necessary. .
Advantages
- Provides a permanent record.
- . Shows the pelvic pathology and the exact site of tubal blockage.
- Dye dislodges the mucus plug and clears the tubal blockage, providing a salvage rate of 30%
Potential Complications
- Anaphylaxis due to an allergic reaction to iodinated contrast material.
- Ascending infection, the spread of tubercular infection.
- Pelvic irritation and pain due to dye (chemical peritonitis).
- Allergic reaction to the dye.
- Pelvic endometriosis if done pre-menstrually or while the woman is bleeding
MAMMOGRAPHY
Mammography is an x-ray test that looks at breast tissue with a low dose of radiation. It is used alongside physical palpation. Mammography is used to check for disease in women over 40, and it is recommended that they get one every year. Mammography is used to look for breast cancer and to check for a wide range of abnormalities in the breast tissue.
The American Cancer Society recommends that all women between the ages of 35 and 40 get a baseline mammogram. Between the ages of 40 and 49, a mammogram should be done every 1 to 2 years, depending on the history of the client.
Indications
- Detects breast mass (benign or cancerous), cysts, abscesses, fibrocystic disease, intraductal papilloma of the breasts, occult cancer, suppurative mastitis, and Paget's disease of the breasts.
- Evaluates the breasts when clinical manifestations are present.
- Screens for women over 40 and for women at risk for breast cancer.
- Ases pendulous breasts that are difficult to palpate
- Provides a method of locating a mass before a biopsy procedure
- Motor diet after breast biopsy and after cancer mag (eg, radio chemotherapy)
Test Procedure
- The client is placed in a sitting or standing position with her breasts famed a congress Allows for correct positioning of the breasts
- Instruct the client to hold her breath when the film is taken. Prevents movement during respiration plastic
Patient Preparation
Before Test
- Explain the test procedure and the purpose of the test Assess the client's knowledge of the test.
- Are the client that radiation exposure is minimal
- Take the consent of the client
- Respect the client's privacy and the sensitive nature of the test, especially if the mammograms nut routine but being conducted because of an abnormal breast examination
- Instruct the client that during the procedure it may be uncomfortable to sit on the hard table to achieve some of the necessary positions. It is important to remain as still as possible during the test. There are no dietary restrictions prior to the test, and it is necessary to remove the dental prosthesis, jewelry eyeglasses, or other metal objects like hair clips before the procedure
During Test
- Adhere to standard precautions
- Provide reassurance and a calm atmosphere during the procedure.
- The client is instructed to take a deep breath and hold it or to exhale and not to breathe as the
After Test
- Recommend that client have a routine mammogram every other year over the age of 40 and annually after age 50.
- Alsa, inform the client that women with an increased risk of breast cancer should have a mammogram annually after age 40.
Contraindications
- Xrays are usually avoided during pregnancy unless the benefit potential risik e fetus outweighs the
Nursing Intervention
- Teach the client BSE (Breast Self-Examination) and provide brochures outlining the procedure and the signs and symptoms to report. Stress the importance of regular mammography depending on the client's age
- Radiation should be avoided in pregnant women if possible.
- Wear lead shielding to protect the fetus if it is determined this is necessary
PAPANICOLAOU SMEAR
The Papanicolaou (Pap) smear or pap test is a screening procedure for cervical cancer. It tests the presence of precancerous or cancerous cells on the cervix. The Papanicolaou (Pap) smear is used primarily in the early detection of cervical cancer. Results of Pap smears are reported in various ways, depending on the laboratory's preference. The traditional method for reporting results is shown here:
- Class I Normal cells only
- Class II Atypical cells but not malignant/inflammatory
- Class III Atypical cells, suspicious of malignancy/mild cervical dysplasia
- Class IV Atypical cells, suggestive of malignancy/severe cervical dysplasia
- Class V Cancer cells present, conclusive for malignancy/cancer
Abnormal results of Pap smears should be followed by either repeat Pap smears or cervical biopsies. It is recommended that women between the ages of 20 and 40 years should have a Pap smear at least every 3 years. Women over the age 40 years should have a Pap smear every year. More frequent examinations may be performed in women who are at high risk for developing cervical cancer (eg. positive family history).
Indications
- Routine screening for cervical cancer.
- Evaluation of estrogen levels and response to therapy with estrogen.
- Identification of inflammatory tissue changes.
- Detection of viral and fungal vaginal infections.
Test Procedure
- Place the client in the lithotomy position with the perineal area exposed. The examiner is seated and has an effective lighting source.
- Select the appropriate-sized vaginal speculum, which has been warmed and lubricated in water, and insert slowly into the vagina and secure it. Lubricant jelly is not used as it will interfere with test results.
- Obtain the cellular sample from the cervical canal with a spatula or brush that is rotated 360°. Rotation provides an opportunity to collect cells from all areas.
- Immediately transfer the sample to the slide(s) and spray or otherwise fix it. Air-dried samples may alter the appearance of cells.
- Label the slides and complete the requisition with the date of the last menstrual period and medication history.
Patient Preparation
Before Test
- Explain to the client that the test should not be performed when the time, The client should not douche or have sexual intercourse for at least 24 hours before de ses has been using an antibiotic vaginal medication, she should discontinue and the test should be delayed for 1 month
- Take the consent of the client that all clothing below the waist be removed (dep smear is to be performed along with a breast examination, it may be necessary to remove clothing and done an examination gown), that the examination will be performed with the dest positioned on a gynecologic examination table
- Tell the diet about slight discomfort when the speculum is inserted during the grocers, and ask to do relaxation and breathing which aid in reducing discomfort during the examination. A breast examination may also be performed as part of the gynecologic evaluation.
- Ensure that the diet voids immediately before the examination
- Obtain a brief gynecologic history that includes the date of the last menstrual period, frequency of periods, duration of periods, type of menstrual flow, date of last Pap smear, and use of control pills or other medications containing hormones
During Test
- Adhere to standard precautions.
After Test
- Instruct the client that she may have a small amount of pink to bloody discharge after the Pap test
Contraindications
- Menstruation
Nursing Considerations
This test is safe during pregnancy for pregnant clients but the cytobrush cell retrieval tool is not recommended for the pregnant diet.
COLPOSCOPY
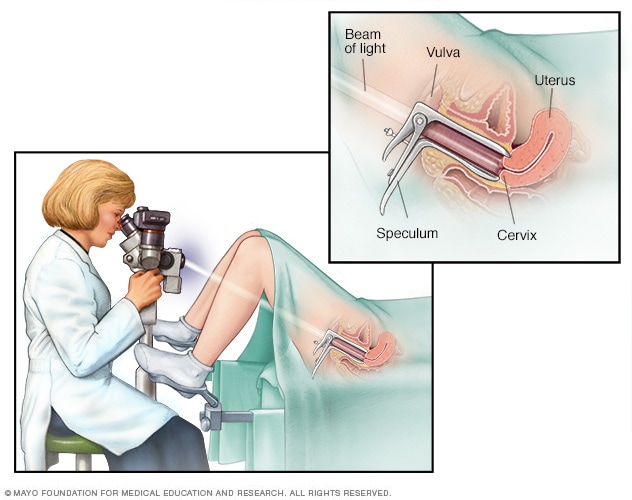
A colposcope is used to look closely at the cervix, vagina, and vulva to look for abnormal cells. This procedure is called an acolposcopy. A colposcopy is a way to see the cervix close up. It is used to find out if there are any abnormal cells on or near the cervix. A colposcope, which is a stereoscopic binocular microscope with low magnification, is used by a health care provider during a colposcopy. The transformation zone is what colposcopy is based on. The transformation zone is the area of the cervix and vagina where columnar epithelium has been replaced by squamous epithelium. This process, called metaplasia, is what makes up the transformation zone. Colposcopy, biopsies, and endocervical curettage are used to find out more about abnormal PAP smears. Depending on the initial results of these tests, the cervix may need to be conized for further testing. Colposcopy is useful for finding a suspicious lesion, but a pathologist needs to look at the tissue to make a final diagnosis. Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) is the name for all epithelial changes in the cervix that are not normal. Malignant epithelial cells are only found in the epithelium and are graded I, II, or III.
Test Procedure
- Place the client in a lithotomy position where a vaginal speculum is inserted to expose the vagina and cervix.
- The cervix is sampled for cytological screening.
- The cervix is cleansed with a 3% acetic acid solution. This removes excess mucous and cellular debris. The acetic acid solution also accentuates the difference between normal and abnormal patterns.
- The cervix is inspected in a clockwise manner.
- Atypical areas are selected for biopsy.
- Endocervical curettage is performed in nonpregnant women.
Indications
- • Evaluates abnormal vaginal epithelial patterns.
- Diagnoses cervical lesions.
- Evaluates suspicious PAP smear results, atypical transformation zone, and dysplasia.
- Evaluates frank invasive carcinoma.
Patient Preparation
Before Test
- Explain the test procedure and the purpose of the test.
- Take the consent of the client.
- Assess the client's knowledge of the test. Provide pre-procedure sedation and analgesia as ordered.
- Transport the client to the procedure room.
- Place the client in a lithotomy position.
- .. Drape the client appropriately.
During Test
- Adhere to sterile technique and standard precautions.
After Test
- Assess for pain and provide pain medication as needed.
- Assess for potential complications.
- Instruct client to abstain from intercourse and not to insert tampon until healing of biopsy is confirmed.
Complications
- Heavy bleeding
- Infection
- Contraindications
- .Heavy menstrual flow
Nursing Considerations
- The onset of early regular sexual activity as a teenager and continued exposure to multiple sexual partners are factors associated with cervical cancer.
- Women from lower socioeconomic class, African Americans, and Mexican Americans are at a higher risk for developing cervical cancer.
- Multiple sexual partners increase the probability of developing cervical intraepithelial neoplasia.
CERVICAL BIOPSY
During a cervical biopsy, a small piece of tissue is taken from the cervix so that abnormal or precancerous cells or cervical cancer can be checked for. When something is wrong during a pelvic exam, a cervical biopsy may be done. It may also be done if a Pap test finds cells that don't look right. If you have an HPVsa type of sexually transmitted infection and your HPV test comes back positive, you may also need a cervical biopsy. Some types of HPV can cause cervical cancer and other less common types of genital cancer. A colposcopy-guided cervical biopsy is a type of cervical biopsy that is done as part of a colposcopy. During a colposcopy, a special instrument with a lens is used to look at the tissues in the cervix.
Types of Cervical Biopsy
Punch biopsy: This procedure uses a circular blade like a paper hole puncher to remove a tissue sample. One or more punch biopsies may be done in different areas of the cervix.
Cone biopsy. This procedure uses a laser or scalpel to remove a large cone-shaped tissue from the cervix
Endocervical curettage: This procedure uses a narrow instrument called a curette to scrape the lining of the endocervical canal. This is an area that cannot be seen from the outside of the cervix.
Indications
- Abnormal Pap smear
- • Schiller test is positive for abnormal cells or tissue.
- The appearance of abnormal cells or tissue (eg, ulceration, leukoplakia, polyps) on colposcopic examination.
- Differentiation of benign from malignant cells or tissue.
- DES (Diethylstilbestrol) exposure
Contraindications
- Acute pelvic inflammatory disease
- Cervicitis
- Bleeding disorder
Test Procedure
- The client is positioned on the examination table. The legs are draped and the external genitalia cleansed with an antiseptic solution.
- For the biopsy, the cervix is swabbed with 3% acetic acid to remove mucus and improve the contrast between tissue types.
- The cervix is swabbed with iodine solution to aid in identification of abnormal cells
- The colposcope is inserted through the speculum and is focused on the cervix.
- If an area is identified as abnormal, the biopsy forceps are inserted through the speculum or colposcope, and tissue samples are obtained.
- The samples are placed in specimen containers with formalin solution. The containers should be labeled with the source of the samples.
- • The vaginal speculum is inserted using water as a lubricant if a Pap smear is to be performed before the biopsy.
- Bleeding, which is not uncommon after a cervical punch biopsy, can be controlled by castery or suturing or by applying silver nitrate or ferric subsulfate to the site.
- . If bleeding persists, a tampon may be inserted by the physician after the removal of the speculum.
Patient Preparation
Explain to the client:
- That the test should not be performed when the client is menstruating and is best performed approximately 1 week after her period has ended.
- Take the consent of the client that all clothing below the waist needs to be removed.
- Take a deep breath during the insertion of the speculum inside the vagina.
- Mild discomfort may be felt by the client while taking small sample of cervical tissue and a small bleeding might occur after the procedure.
- The gray-green discharge may persist for a few days to a week.
- Avoid strenuous exercise for a day after the procedure.
- Avoid douching and intercourse for about 2 weeks after the procedure.
Prepare for the procedure;
- Explain the procedure to the client.
- Ensure that the client voids immediately before the procedure.
- Anticoagulants should be stopped or the dose should be minimized as ordered before the test.
- Tampons, vaginal creams, medicines, douches should not be used for 24 hours before the procedure.
- Avoid sex 24 hours before the procedure.
- Patients may require pain relievers (take 30 min before the procedure).
- Patients should bring sanitary pads to wear home after the procedure.
Nursing Consideration
Assist the client to remove the legs from the stirrups and allow her to rest for a while.
FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION CYTOLOGY (FNAC)
Fine needle aspiration (FNA)/ FNAC is a quick and simple procedure that removes fluid or cells from a breast lesion or cyst (a lump, sore, or swelling) using a fine needle similar to a blood sample needle to diagnose or rule out malignancy. If fluid is extracted, it is placed on a slide, while tissue is deposited in a sterile container. Under a microscope, a cytologist can also study frozen-section samples. A FNA is conducted to ascertain the nature or diagnosis of the lesion and, if necessary, to arrange therapy. Breast FNA may also be performed to aspirate a cyst (i.e., withdraw fluid from the cyst) in order to entirely eradicate it or alleviate discomfort if the cyst is big and painful.
If the lesion cannot be felt from the surface of the skin, the doctor may use guidance for the FNA by using ultrasound images or pictures. This shows an image of the inside of the breast on a screen to allow the doctor to ensure the needle is going into the lesion. Alternatively, this can be done under stereotactic (mammography) guidance if the lesion has only shown up on a mammogram. Stereotactic guidance involves the insertion of the needle after a three-dimensional view is obtained by mammography and computers. The abnormal tissue is located and a sample is then taken,
List of Equipment
- Povidone-iodine
- Dry sterile dressing
- Transport container
- Biopsy tray
- Needle
- Local anesthetic
- Slides
Indications
- Evaluates abscesses, cysts, mastitis, calcification, and fibrocystic disease.
- Diagnoses carcinoma conditions of the breast.
Test Procedure
- Confirm correct breast with client and chart to prevent biopsy from the incorrect site.
- Cleanse the breast tissue with povidone-iodine and drape the breast to maintain aseptic technique.
- Anesthetize sites and obtain biopsy samples.
- Evaluate the sample on slides or in a sterile container.
- Apply a dry sterile dressing over the puncture site to prevent infection.
Patient Preparation
Before Test:
- Explain the test procedure and the purpose of the test.
- Clients may experience vertigo during the procedure; therefore, monitor for early signs and symptoms, such as lightheadedness, vertigo, pallor, and diaphoresis.
- Take the consent before the procedure. Also, specimens must be sent to the laboratory immediately after obtaining them.
- Explain the test procedure and the purpose of the test.
- Assess the client's knowledge of the test.
- Provide pre-procedure sedation and analgesia as ordered.
- Transport client to operating or procedure room and drape the client appropriately. Instruct client to remain NPO for 8 hr before the test if a general anesthetic is to be used.
During Test:
- Adhere to sterile technique and standard precautions.
- Provide reassurance and a calm atmosphere during the procedure.
- Confirm with the client and chart which breast is being biopsied.
- Monitor for signs of syncope.
After Test:
- Clean site of biopsy.
- Provide analgesia as necessary.
- Take vital signs frequently.
- Provide emotional support and encourage normal activity.
- Educate the client to use warm, moist compresses for pain and to wear a supportive bra.
- Teach client signs and symptoms of infection.
Potential Complications
- Bleeding and bruising at the site; cellulitis
Nursing Intervention
- The older person may find it difficult to maintain positions when required to do so for lengthy periods during the biopsy.
Before the Test
- Confirm the patient's identity according to facility policy.
- Describe the procedure to the patient, and offer her emotional support, and assure her that breast masses don't always indicate cancer.
- Inform the patient scheduled for a needle biopsy that she'll need to sit still during the procedure.
- If the patient is to receive a local anesthetic, advise her that she doesn't need to restrict food, fluids, and medication. If she's to receive a general anesthetic, advise her to fast from midnight before the procedure until after the biopsy.
- Tell the patient who will perform the biopsy, and where and when it will be done. Explain that pretest studies, such as blood tests, urine tests, and chest X-rays, may be required.
- Make sure the patient or a responsible family member has signed an Informed consent form. Check the patient's history for hypersensitivity to anesthetics.
During the Test
- Remind the patient undergoing a needle biopsy to sit still.
- Assist with the collection of specimens into the appropriate containers, if indicated.
- Send the specimens to the laboratory immediately, if appropriate.
After the Test
- If the patient has received a general or local anesthetic, monitor the patient's vital signs regularly.
- If she has received a general anesthetic, check her vital signs every 15 minutes for 1 hour, every 30 minutes for 2 hours, every hour for the next 4 hours, and then every 4 hours.
- Administer analgesics for pain, as ordered, and provide ice bags for comfort.
- Instruct the patient to wear a support bra at all times until healing is complete.
- Observe for and report bleeding, tenderness, and redness at the biopsy site.
- Provide emotional support to the patient awaiting diagnosis.
HIGH VAGINAL SWAB
A high Vaginal Swab (HVS) is a technique used to obtain a sample of discharge from the vagina. This is then sent for culture and sensitivity. It is commonly used to test for the presence of candidiasis infection, bacterial vaginosis and trichomonas vaginalis.
List of Equipment
- Vaginal speculum
- Glass slides
- Long cotton swabs
- Coplin jar of 95% ethanol
Nursing Intervention
Before the Test
- Explain to the client
- The samples will be collected through vaginal examination.
- The use of lubricant during intercourse and of douching after intercourse should be avoided.
- The positioning on the pelvic examination table needs to be explained.
- If saline lavage is used to collect the sample, the client may experience a sensation of coldness.
- Procedure Preparation
- Assist the client in putting on an examination gown.
- Advise the client to void before the procedure.
- Privacy should be maintained during the examination.
Test Procedure
- The necessary equipment is assembled, including vaginal speculums, Papanicolaou sticks, cotton-tipped applicators, gloves, saline and syringes for lavage (if necessary), slides, and small jars containing 95% ethanol
- The client is assisted to the lithotomy position on the pelvic examination table. Maintain privacy and drape the patient.
- Insert speculum.
- With a long cotton swab, scrape the vagina wall to obtain specimens. A vaginal speculum is inserted and the specimen is obtained by direct smear, aspiration, or saline lavage. The sterile swab is inserted into the vagina and takes the swab by rolling the swab without overlapping the vaginal wall near the cervix.
- Dry the swab stick and insert it into the tube without touching anywhere on the tube's cover. The specimens are labeled with name, time of collection, and source of the specimen and transported to the laboratory to identify the client and the test to be performed.
TRANSVAGINAL SONOGRAPHY
Transvaginal ultrasound is an imaging scan used to look at a woman's reproductive organs, including the uterus, ovaries, and cervix. Transvaginal means across or through the vagina. The ultrasound probe will be placed inside the vagina.
Indications
- Abnormal findings on a physical exam, such as cysts, fibroid tumors, or other growths. Abnormal vaginal bleeding and menstrual problems
- Infertility
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Pelvic pain
- Transvaginal ultrasound is also used during pregnancy
Test Procedure
- Help the patient to undress to put on the examination gown and maintain privacy.
- Place the client in the lithotomy position.
- The probe called a transducer is placed into the vagina. The probe is covered with a condom and a gel.
- The probe sends out sound waves, which reflect off body structures. A computer receives these waves and uses them to create a picture.
- The radiologist doctor can see the picture on a TV monitor and will move the probe around the area to see the pelvic organs.
- In some cases, a special transvaginal ultrasound method called saline infusion sonography (SIS) may be needed to view the uterus.
Patient Preparation
Before Test
- Ask the patient to go to the bathroom. The bladder may need to be emptied before the test.
- Ask the patient whether she is under any natural therapies or anticoagulant, or has had any pelvic surgery.
During Test
- Ask the patient to change into a hospital gown and then lie down on an exam table with your knees raised, as you would for a pelvic exam.
- A thin hand-held probe shaped like a tampon with a sterile cover and non-greasy gel is put inside the vagina. In some cases, the patient is asked to put the probe in herself.
- The sonographer will move the probe to get the best picture. Patients may sometimes feel pressure. Ask the patient to tell the sonographer if she feels pain.
After Test
- Before leaving, the patient may need to wait for a short time while the images are reviewed. Patients can go back to their normal routine right after the test. Healthcare providers will wait until the results of the test are ready.
- Healthcare provider will explain the results to the patient.
Things to remember
- Assess the client's knowledge of the test.
- Place the client in the lithotomy position with the perineal area exposed.
- Fine needle aspiration (FNA)/ FNAC is a quick and simple procedure that removes fluid or cells from a breast lesion or cyst (a lump, sore, or swelling) using a fine needle similar to a blood sample needle to diagnose or rule out malignancy.
- If the patient has received a general or local anesthetic, monitor the patient's vital signs regularly.
- Place the client in the lithotomy position.
Questions and Answers
Define Hysterosalpingography.
Fluoroscopy, a specialized form of X-ray, is used in hysterosalpingography, an X-ray examination of the uterus and fallopian tubes after the injection of a contrast agent. The location, size, and shape of the uterus and fallopian tube are all revealed by this examination. It is possible to carry out the procedure to find fistulas and polyps. The fallopian tubes, which transport the egg from the ovary to the uterus, are most frequently examined to see if they are open. When determining a patient's potential to become pregnant, this conclusion is crucial.
What do you mean by Trans-vaginal sonography ?
Trans-vaginal sonography is a technique used to see within the vagina to check the condition of the uterus, fallopian tubes, ovary, uterine ligaments, and other reproductive organs. This is comparable to ultrasound, where sound waves are used to record images once the probe is placed into the vagina. It is frequently utilized for diagnostic as well as screening purposes, including follicular monitoring, endometrial lining monitoring, and other screening.
Define Colonoscopy.
Colonoscopy is the use of a light source and a binocular microscope to directly magnify and examine the surface of a woman's vaginal area, including the cervix, vagina, and vulva. This test is done to assess areas that may be malignant, often after a pap smear has suggested that there may be a concern. During colposcopy, a biopsy from the abnormal region may be taken.
What do you mean by laparoscopy and list down the indication of laparoscopy ?
By using a laparoscope, the peritoneal cavity can be seen clearly. Using a laparoscope, the ovaries can be seen outside of the tubes and uterus. The laparoscope is a device that uses fiber optics to illuminate the abdomen. Its length is double that of a fountain pan and its circumference is similar.
A special needle is inserted immediately below the umbilicus during a surgery to provide carbon dioxide to the abdomen. During a laparoscopy, this gas helps to separate the internal organs of the abdominal cavity, making it simpler to see the reproductive organs. At the conclusion of the procedure, the gas is expelled.
Indications:
- Pelvic pain
- Infertility
- Endometriosis
- Tubal ligation
- Tubal pregnancies
- Pelvic inflammatory disease
- Repairing damaged fallopian tube
- Removal of ovarian cyst or the entire cavity.
What is the indication of hysterosalpingography?
Indication
- To assess the uterus's anatomy and form, the fallopian tube's openness, and any peritoneal cavity scarring
- To assess the impact of tubal ligation, consider:
- Thoracic ligation
- The closing of the fallopian tubes during sterilization and the undoing of sterilization.
- Identifying the presence and severity of uterine congenital anomalies in order to study frequent miscarriages caused by these defects, including
- A mass of cancer or adhesion
- Uterine tumors
Define mammography .
A special kind of imaging called mammography employs a low-dose x-ray to check the breasts. A mammogram, often known as a mammography examination, is used to help women diagnose breast disease.
An X-ray is a painless diagnostic tool for identifying and treating medical issues. A modest dosage of ionizing radiation is applied to a body part during radiography to provide an image of the interior of the body. Computer-aided detection and digital mammography are two recent improvements over conventional mammography.
What are the patient preparation of mammography ?
Preparation for a mammography:
- Ask about any prior operations, hormone use, and any personal or family history of breast cancer.
- One week after the last menstrual cycle is the ideal time for a mammogram.
- Always let the doctor or X-ray technician know if there's a chance of pregnancy.
- On the day of the exam, avoid using deodorant, talcum powder, or lotion on your breasts or beneath your arms. These might show up as calcium spots on the mammogram.
- Any breast symptoms or issues should be explained to the technologist conducting the assessment. If at all feasible, get mammograms and provide them to the radiologist at the present examination.
- Inform the patient that a small amount of pain may occur when the breast is compressed, and that the pain can be reduced by taking the following action.
- They are in charge of the breast compression during mammography.
- Utilize relaxing self-statements and discover mammography distraction strategies..
Define high vaginal swab and its purpose ?
To rule out infection, a high vaginal swab method is used to collect a sample from the vagina.
Purposes:
There will be a high vaginal swab taken:
- From all females exhibiting unusual vaginal discharge.
- From a gynecological or obstetric post-operative with an unknown pyrexia
- Among all pregnant women who appear with an early membrane rupture
- Prior to the implantation of an intrauterine device.
- Before the cervical cerclage was inserted.
What is the cervical biopsy refers to and how can we prepare patient for cervical biopsy procedure ?
During a cervical biopsy, tissue from the cervix is removed in order to be examined for abnormalities, precancerous diseases, and cervical cancer.
Patients preparation
- Give the patient an explanation of the operation and give them the chance to ask any questions they may have about it.
- Please accept.
- If you are sensitive to or allergic to any medications, latex, tape, iodine, or anesthetic agents, let your doctor know.
- The patient should wait 24 hours before the surgery to use tampons, vaginal creams, etc.
- void one's bladder.
- In order to reveal the cervix, the doctor will introduce a speculum into the vagina and spread its walls apart.
- Colposcope can be used to magnify cervical tissue.
- A vinegar solution, commonly known as an acetic acid solution, can be used to clean and soak the cervix.
- The size, shape, location, and other features of the anomaly will dictate the sort of biopsy that is carried out.
- Wear a sanitary pad after the operation to prevent bleeding
- For many days, take a pain reliever for cramping, spotting, and dark or black discharge.
- After a biopsy operation, you shouldn't douche, use tampons, or have sexual relations for a week.
- If you experience any of the following, tell your doctor right away:
- Bleeding
- Foul- smelling drainage from your vagina
- Fever and /or chills
What is the patient preparation of laparoscopy ?
Patient preparation
Before the procedure:
- Give the patient a description of the process and give them the chance to ask any questions they may have about it.
- Get permission.
- 8 hours before the surgery, keep NPO.
- It is possible to shave the area of the abdomen where the incision will be made (part preparation)
- A few hours before to the surgery, you might administer a cleansing enema.
During the procedure:
- Take off any jewelry or other items that might get in the way of the treatment.
- Take off your clothes and put on a gown.
- Intravenous (IV) line that is open
- To lessen the risk of bladder perforation, a bladder-indwelling catheter may be placed.
- Just below the umbilicus, a tiny incision will be made in the abdomen.
- The abdominal cavity will be inflated with carbon dioxide gas to make it easier to see the organs and other structures.
- After inserting the laparoscope, the procedure for the examination will begin.
- The laparoscope will be taken out after the examination and any extra procedures have been finished.
- With stitches or surgical staples, the incision will be closed.
- It will be covered with an adhesive bandage, dressing, or sterile bandage.
After procedure:
- Within a few hours of the treatment, allow to drink clear liquids.
- Consult a doctor if any of the following symptoms appear:
- Fever and /or chills
- Redness , swelling or bleeding or other drainages from the incisions site
- Increased pain around the incision site
- Vomiting
- Difficulty with urination
Write how can we prepare patient ?
- To ensure that women are not pregnant during the exam, the hysterosalpingography procedure is best done one week after menstruation but before ovulation.
- Take a laxative or an enema to clear your system the night before the surgery so that the uterus and its environs may be seen properly.
- Mild sedatives or over-the-counter medications may be used before to the treatment to reduce any potential discomfort.
- Identify any allergies you may have to contrast materials.
- Remove any jewelry, eyewear, or clothes made of metal that could obstruct the X-ray pictures.
- On the exam table, the patient should be lying on her back with her legs drawn up to her chest or her feet raised in stirrups.
- The catheter is put into the cervix after a speculum is inserted into the vagina.
- The patient is carefully positioned beneath the fluoroscopy instrument once the speculum is removed.
- After taking fluoroscopic images, the contrast material starts to fill the uterine cavity through the catheter.
- The catheter will be taken out after the treatment is finished, and the patient can then sit up.
Define pap smear and how the procedure is preformed ?
A pap smear, also known as a pap test, involves taking cells from the cervix to be tested for any anomalies that could be cervical cancer or diseases that could lead to cancer in females.
Every woman who has attained the age of 21 or who has ever engaged in sexual activity should get a pap smear every year. It is the finest technique for finding small, concealed lesions that may develop into cervical cancer as well as pre-cancerous conditions. Cervical cancer is curable if caught early.
During the pap smear:
- Only the waist down should be undressed entirely.
- Keep the patient on an examination table in the lithotomy position.
- Put a speculum in the vagina with care. The examiner can clearly see the cervix because the speculum keeps the vaginal walls apart. A pressing sensation in the pelvic area could result from speculum insertion. When first inserted, the speculum might occasionally feel frigid.
- After that, collect cervical cell samples from an endocervical region using a soft brush and a flat scraping tool known as a spatula (junction between cervix and external os). The sample being collected is not painful and you might not even notice it.
Explain the patient preparation for the FNAC procedure ?
Preparation of the patient
Explain the following procedure:-
- The test's objective
- How and by who the test will be administered
- When it will take place
- Whether there are any clinical conditions that could prevent the test from being conducted (eg, comorbid medical , allergies , current use of anticoagulant medication)
- Potential test-related issues, such as bruising
- Test costs for the females.
During procedure
- The women are positioned comfortably, typically supine.
- Cleanse the skin around the lesion.
- Over the lesion, local anesthetic is injected into the skin.
- Between the thumb and fingers of one hand, the lesion is immobilized. The outside hand is used to insert the needle. The needle may be inserted on its own, with the syringe attached, or with the syringe and holder attached, depending on the operator's preference.
- Negative pressure is exerted as the needle is inserted into the lesion until it is perceived to be at the lesion's edge.
- While the needle is inside the lesion, the negative pressure is discharged. The needle is then withdrawn and the material is expelled from the needle onto a labeled glass slides using the syringe
© 2021 Saralmind. All Rights Reserved.

 Login with google
Login with google