Sub Fertility
Subject: Gynecological Nursing

Overview
Between 3 and 7% of all couples or women have an unresolved problem of infertility. Infertility problems affect 1 in 7 couples in the UK. Both women and men can have problems that cause infertility. There is no one definitive factor that causes infertility. The term infertile should not be used until pregnancy is impossible.
Infertility can occur as a result of some conditions. Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a condition that often inhibits the ovaries from producing an egg. For men, the most common cause of infertility is abnormal semen, accounting for 75% of all male infertility cases. Couple Instruction: Infertility, Coital problems, General improvement of health and Medications used to treat infertility in women and Male Infertility. Intra Cytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI) can be helpful in cases of male factor infertility.
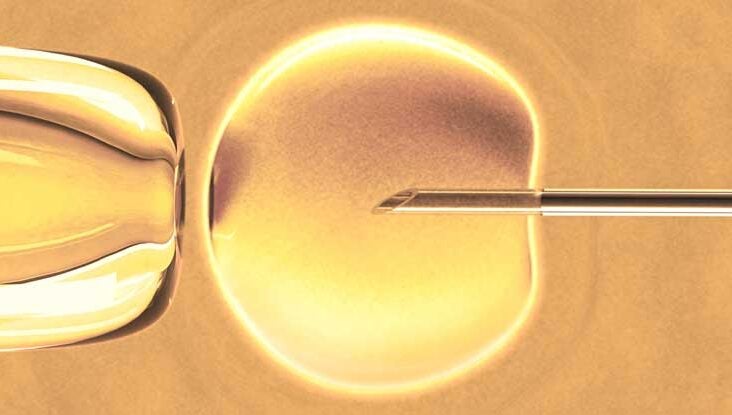
A single sperm is extracted from the ejaculate, the testis, or the epididymis. It is inserted into the egg with the aid of a microneedle.
Introduction
Infertility is fundamentally the inability to conceive a baby. Infertility also refers to the state of a woman who is unable to carry a pregnancy to full term. About 40 percent of the issues involved with infertility are due to the man, another 40 percent due to the woman, and 20 percent result from complications with both partners.
Prevalence of infertility
- Worldwide between 3 and 7% of all couples or women have an unresolved problem of infertility.
- Many more couples, however, experience involuntary childlessness for at least one year: estimates range from 12% to 28%.
- Fertility problems affect 1 in 7 couples in the UK.
- A study conducted by UNFPA in eight districts of Nepal found 7.4% of females have infertility problems.
- Among the women who were reported infertility 40% have tried one or other forms of traditional remedies for infertility (herbs, special foods, dhamijhakri and special puja) (UNFPA, cited from Shrestha D.R, 2012)
Definition
According to WHO a couple is described as infertile if the woman has not gotten pregnant after having normal sexual intercourse two or three times a week without using any contraception for at least one year. The term infertile, strictly speaking, should not be used until it is proved that pregnancy is impossible.
WHO has further defined various types of infertility as follows:
- Primary infertility: The couple has never conceived despite regular (2-3 times per week) unprotected intercourse for at least 12 months (1 year).
- Secondary infertility: The couple previously had conceived but is now unable to do so despite 12 months of unprotected intercourse.
- Sub-fertility: The couple has difficulty in conceiving jointly because both partners may have reduced fertility.
- Pregnancy wastage: The woman can conceive but is unable to produce a live birth (unable to carry the pregnancy long enough to deliver a living child).
Is infertility just a woman's problem?
No, infertility is not always a woman's problem. Both women and men can have problems that cause infertility. There is no one definitive factor that causes infertility.
Causes of Infertility in Women :
- Anovulation: Ovulation is vital to pregnancy, and without the monthly release of an egg there will be nothing for the male sperm to combine with. Failure to ovulate for whatever reason is one of the most common causes of infertility.
- Tubal factors:
- Impaired tubal motility,
- Loss of cilia,
- Defective ovum pick-up &
- Blocked Fallopian tubes due to pelvic inflammatory disease, salpingitis, endometriosis, or surgery for an ectopic pregnancy
- Periesophageal adhesion
- Uterine factors
- Uterine fibroid
- Endometriosis
- Uterine neoplasm
- Uterine hypoplasia
- Congenital malformation
- Cervical factors
- Congenital elongation
- Acute retroverted uterus
- Second-degree uterine prolapsed
- Cervical polyps/tumors
- Excessive viscosity of cervical mucous
- Cervicitis
- Vaginal factors- Atresia, transverse septum, vaginitis, chronic infections of the vagina
Infertility can also occur as a result of some conditions below:
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): This is a condition that often inhibits the ovaries from producing an egg.
- Early menopause: A women's ovaries stop working before she reaches the age of 40.
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
- Endocrine disorders, Pituitary, Thyroid, and Adrenal problems
- Chronic long-term illnesses such as diabetes, cancer, or kidney failure may not ovulate.
- Cushing syndrome: A hormonal disease that can stop the ovaries from releasing an egg.
Causes of Male infertility
For men, the most common cause of infertility is abnormal semen, accounting for 75% of all male infertility cases. Some of the conditions are
- Low sperm count & sperm mobility
- Abnormal sperm
- Varicocele
- Ejaculation disorders
- Bacterial or viral infection of seminal vesicle & prostate gland, prostatitis, TB, gonorrhea, surgical trauma
- Absence of vas deference
Defective spermatogenesis: Undescended testes, orchitis
Coital difficulties: Chordee (painful, downward curving erection)
Agenesis or destruction of testes, cryptorchidism, torsion of the testes Hypospadias, Urethral stricture
Prostate and seminal vesicle abnormalities: Chronic prostatitis, seminal vesiculitis
What increases a man's risk of infertility?
- Heavy alcohol use
- Drugs: cytotoxic, antihypertensive, B-blockers, antidepressants, anticonvulsants etc. Environmental toxins, including pesticides and lead
- Smoking cigarettes
- Health problems such as mumps, kidney disease, or hormone problems, malnutrition, cancer
Factors affecting fertility of both sexes
Age
- According to statistics, the biggest drop in fertility levels occurs during our mid-thirties. For women who are aged 35, 95% will fall pregnant within three years of having regular unprotected sex.
- For women who are 38, this figure falls to 75%.
- With regards to male age and fertility, it is thought that men over the age of 35 are half as likely to achieve conception in comparison to men younger than 25.
Stress
- Stress does have a direct impact upon fertility by limiting the production of sperm in men, whilst also affecting ovulation within females
Weight
Being outside of a healthy weight range can seriously impact fertility. Women who are overweight or severely underweight for example will often find that their ovulation is affected, or in some cases, it may stop entirely.
Diagnosis and treatment of Infertility
For male:
- Semen analysis
- Serum FSH, LH, testosterone, prolactin, TSH
- Routine urine & blood investigation, blood sugar level
- USG- to visualize seminal vesicle, prostate gland, ejaculatory duct
- Chlamydia test and genetic testing
For female:
- Cervical mucous study
- Vaginal cytology
- Hormone estimation- serum progesterone, LH
- Hysterosalpingography
- Endometrial biopsy
- Chlamydia test and genetic testing
- USG
INFERTILITY TREATMENT
There are three main types of fertility treatment available:
- Treatment to assist fertility
- Surgical procedures
- Assisted conception, which may be intrauterine insemination (IUI) or In-vitro fertilization (IVF)
Couple Instruction
- Assurance
- To obtain body weight at an optimum of BMI 20-24.
- Avoid smoking & alcohol consumption.
- Coital problem: advice to have intercourse during the midcycle & minor psychological problem should be corrected accordingly
Treatment of male infertility
- Improvement of general health problem.
- Avoidance of tight warm undergarments
- Avoidance of too frequent intercourse may at times improve the sperm count.
- Supplementation of vitamin E, C, B12, & folic acid.
- Antibiotics can also be used to clear up infections affecting sperm count.
- Sperm movement: Sometimes semen has no sperm because of a block in the man's system. In some cases, surgery can correct the problem.
Treatment of female Infertility
- General improvement of health
- Psychotherapy for emotional problem
- Advice on the timing of intercourse
- Surgical management e.g. Tuboplasty, myomectomy, enlargement of vaginal introitus & removal of vaginal septum
Prevention of Infertility
- Prevent from STIS
- Maintain healthy practices
- Avoid unnecessary drugs
- Protect scrotum from heat
- Prevent from other infections Avoid chemicals
ASSISTED REPRODUCTIVE TECHNOLOGY (ART)
ART is a general term referring to methods used to achieve pregnancy by artificial or partially artificial means. It is reproductive technology used primarily in infertility treatments. The term includes any reproductive technique involving a third party e.g. a sperm donor.
Some of the ARTS are mentioned below;
Ovulation induction
- Medicines used to treat infertility in women:
- Clomiphene citrate
- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (Gn-RH) analog
- Human menopausal gonadotropin or hMG
- Follicle-stimulating hormone
- Bromocriptine
Intrauterine insemination (IUI)
- Insertion of washed semen directly inside the uterus through the cervical canal by using a syringe and cannula.
- In vitro fertilization (IVF) and Embryo Transfer
- This is one of the most commonly used procedures. Ovum is combined with a partner's sperm in a dish in a laboratory. Once fertilization has occurred, the resulting embryos develop for 3 to 5 days before being placed in the uterus. One cycle of IVF takes about two weeks.
Risks of IVF Treatment
Specific steps of an in vitro fertilization (IVF) cycle carry risks, including:
- Multiple births
- Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (pain, bloating, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea)
- Premature delivery and low birth weight
- Miscarriage
- Egg-retrieval procedure (bleeding, infection, or damage to the bowel, bladder or blood vessel)
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Birth defects
- Ovarian cancer
- Stress (financially, physically, and emotionally)
Success Rates for In Vitro Fertilization
The live birth rate for one cycle varies by maternal age: 30% to 35% among women younger than 35 years of age and 25% for those aged 35 to 37 years. The success rate ranges from 6 \%-10\% in those older than 40 years of age. Pregnancy in women older than 44 years of age is rare.
The rate of miscarriages with IVF pregnancies is the same as that with normally conceived pregnancies. An ectopic pregnancy occurs in about 3% to 5% of cases.
Donor egg or embryo
If the client's unable to conceive using her own eggs, an egg donated by another woman is mixed with the patient's partner's sperm and the resulting embryo is implanted in the client's uterus. This procedure also can be done with a donated embryo or sperm.
Gamete Intra Fallopian Transfer (GIFT)
In this procedure, both the sperm and unfertilized oocyte are transferred into the fallopian tubes using laparoscopy following transvaginal ovum retrieval. Fertilization is then achieved in vivo.
Zygote Intra Fallopion Transfer(ZIFT)
Here, a woman's egg cells are extracted from her ovaries and fertilized artificially. Once the zygote has formed, it is transferred into the fallopian tube by laparoscopy or the uterine incision using ultrasound guidance. When the problem is in a male factor, or if GIFT has already been attempted and failed, this method is a viable backup plan. In cases where tubal factor infertility is present, neither GIFT nor ZIFT should be attempted.
Intra Cytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI)
When the sperm count is low or IVF attempts have failed, this can be helpful in cases of male factor infertility. In this technique, a single sperm is extracted from the ejaculate, the testis, or the epididymis and then inserted into the egg with the aid of a microneedle.
Surrogacy, or use of a gestational carrier
Another woman carries the embryo of the client, or a donor embryo, to term and gives the baby to the client after birth.
Prognosis of Artificial Reproductive Method
Thirty to forty percent of couples became pregnant during the course of the study, or within two years after its initiation. If the pregnancy does take place, however, the risk of miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, and perinatal mortality all increase by a factor of two.
Things to remember
- It is reproductive technology used primarily in infertility treatments.
- The rate of miscarriages with IVF pregnancies is the same as that with normally conceived pregnancies.
- This procedure also can be done with a donated embryo or sperm.
- Intra Cytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI) When the sperm count is low or IVF attempts have failed, this can be helpful in cases of male factor infertility.
- If the pregnancy does take place, however, the risk of miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, and perinatal mortality all increase by a factor of two.
Questions and Answers
Define infertility and its types?
A couple who wants a child but is unable to conceive after 12 months of unprotected sexual activity is said to be experiencing infertility. Not being able to bring a pregnancy to term is included in a more inclusive definition of infertility. WHO's definition is as follows:
- Primary Infertility
- Despite having regular (2–3 times per week) unprotected sex for at least a year, the couple has never conceived.
- Secondary Infertility
- Despite 12 months of unprotected sexual activity, the couple has been unable to conceive in the past.
- Sub- Fertility
- Due to possible reduced fertility in both partners, the couple struggled to conceive.
- Pregnancy Wastage
- The woman can conceive, but she cannot give birth to a live child ( (unable to carry the pregnancy long enough to deliver a living child).
What are the causes of female infertility?
Ovulation Disorders
In roughly 25% of infertile couples, ovulation abnormalities, which result in sporadic or nonexistent ovulation, are the cause of infertility. These can be brought on by issues with the ovary itself, as well as issues with the hypothalamus' or pituitary gland's control of reproductive hormones.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
- A hormone imbalance that impairs ovulation results from complicated alterations in the brain, pituitary gland, and ovaries in PCOS. PCOS is linked to insulin resistance, obesity, abnormal body or facial hair development, and acne. It is the most frequent reason for infertility in women.
- Hypothalamic Dysfunction
- Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH), the two hormones that trigger ovulation each month, are produced by the pituitary gland in a particular pattern throughout the menstrual cycle. This pattern can be broken and have an impact on ovulation if there is too much physical or emotional stress, extreme body weight swings, or a recent significant weight gain or loss. The main indicator of this issue is inconsistent or missing periods.
- Premature Ovarian Insufficiency
- This condition is typically brought on by an autoimmune reaction in which your body mistakenly attacks ovarian tissues or by the early loss of eggs from your ovaries as a result of genetic issues or environmental insults like chemotherapy. The ovary loses its capacity to produce eggs as a result, and estrogen production declines in women under the age of 40.
- Too Much Prolactin
- Less frequently, the pituitary gland can increase prolactin production (hyperprolactinemia), which inhibits the production of estrogen and may result in infertility. The most typical cause of this is a pituitary gland issue, but it may also be related to drugs you're taking for another illness.
Damage to Fallopian Tubes (Tubal Infertility)
Fallopian tubes that are damaged or blocked prevent sperm from reaching the egg or prevent the fertilized egg from entering the uterus. The following list of factors may contribute to fallopian tube damage or obstruction:
- An infection of the uterus and fallopian tubes brought on by chlamydia, gonorrhea, or other sexually transmitted illnesses is known as pelvic inflammatory disease.
- Prior abdominal or pelvic surgery, such as that performed for an ectopic pregnancy, in which a fertilized egg implants and begins to develop in a fallopian tube rather than the uterus.
- Pelic tuberculosis, although rare in the United States, is a significant contributor to tubal infertility globally.
Endometriosis
When tissue that ordinarily develops in the uterus implants and spreads to other areas, endometriosis results. The surgical excision of this excess tissue growth may result in scarring, which may clog the tube and prevent the egg and sperm from fusing. Additionally, it can harm the uterine lining, preventing the fertilized egg from implanting properly. The illness also appears to harm sperm or eggs, which would have a less obvious impact on fertility.
Uterine or Cervical Causes
A number of uterine or cervical conditions can affect fertility by preventing implantation or raising the risk of miscarriage.
- The uterus frequently harbors benign polyps or tumors (fibroids or myomas), and some of these growths might reduce fertility by obstructing the fallopian tubes or interfering with implantation. Many women with fibroids or polyps can still get pregnant, though.
- Implantation can be hampered by endometriosis scarring or uterine inflammation.
- Obstacles to attaining or maintaining pregnancy might result from uterine anomalies that are present from birth, such as an abnormally shaped uterus.
- A hereditary deformity or cervix injury can lead to cervical stenosis, a narrowing of the cervical canal.
- There are occasions when the cervix is unable to create the ideal kind of mucus to allow the sperm to pass through and enter the uterus.
Unexplained Infertility
Sometimes an infertile cause is never identified. It's likely that these unexplained reproductive issues are caused by a confluence of multiple minor conditions in both partners. Even though it is annoying to not receive a definitive response, this issue might get better over time.
What are the management and the causes of female infertility?
Management of Female Infertility
According to the disorders, the treatment options for female infertility are categorized as follows:
- Ovular factors
- Induction of ovulation
Clomiphene citrate has been used frequently to stimulate the ovaries alone or in various combinations.
- From D3 to D7, use clomiphene citrate (50/100/150mg) everyday. At the LH surge, inject hCG (5000 IU).
- Daily doses of clomiphene citrate (950/100/150mg) from D3 to D7 plus injections of HMG (75IU) from D3 to D7 and HMG ((75IU) from D8 to D10 are then given, and finally an injection of hCG (55000IUU) is given at the time of LH surge.
- Intra-uterine insemination (IUI) eliminates the requirement for sperm to travel from the vagina to the uterus by immediately inserting a prepared semen sample with sufficient quantities of motile, healthy sperms suspended in a nutritional medium into the uterine cavity. This is carried out at the anticipated ovulation time. The husband's or a donor's sperm should be used for insertion.
Tubal/Peritoneal Factors
The following are some potential tubal causes of infertility:
- Adhesion to the abdomen
- Inflammation of the endosalpinges
- By infection or sterilization, tubal occlusion
The surgical process known as tuboplasty, sometimes known as microsurgical procedures, also comprises adhesiolysis, fibrinolysis, salpingostomy, tubo-tubal anastomosis, and tubo-cornuaal anastomosis. Prophylactic antibiotics, intraoperative RL instillation alone or combined with heparin or hydrocortisone, or postoperative hydrotubation are examples of adjunctive procedures to improve the outcome of tubal surgery.
- Cervical Factors
- Sperm are shielded by cervical mucus from both phagocytosis and the hostile environment of the vagina. Weak alkaline douching or conjugated estrogen 1.25 mg taken orally during the follicular stage can both improve the quality of cervical mucus.
- Immunological Factors
- For anti-sperm antibodies in the cervical mucus during the follicular phase, use dexamethasone 0.5 mg before night. It might lessen anti-sperm antibodies, which would make sperm entry easier. Throughout the fertile phase, a couple should encourage regular sexual activity. An alternative is intrauterine insemination using cleaned sperm.
- Unexplained Infertility
- It is strange that four out of ten couples who do not receive any special care become pregnant within three years. Before using ART, IUI, IVF, or other techniques, one should wait for a specific amount of time due to the spontaneous cure rate.
- Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART)
- Is the technology used in methods including fertility treatment, artificial insemination, in vitro fertilization, and surrogacy to bring about conception. It is reproductive technology, also referred to as a fertility treatment, that is primarily used to treat infertility. It mostly relates to reproductive endocrinology and infertility, and it may also involve cryopreservation and intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI). For genetic reasons, several ART methods are also used to fertile couples (pre-implantation genetic diagnosis). When a pregnancy is desired but a couple is at risk for contracting a certain communicable disease, such as HIV, ART is also used to lessen that risk.
© 2021 Saralmind. All Rights Reserved.

 Login with google
Login with google