Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) and Ribonucleic Acid (RNA)
Subject: Science

Overview
DNA, a long, thread-like molecule, contains genetic information within cells and chromosomes. It is made up of nucleosides and nucleotides, with different nucleotide sequences. DNA carries genes, which are passed down through generations. RNA, a polynucleotide, is single-stranded and partially present in chromosomes. It aids in protein synthesis in viruses.
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
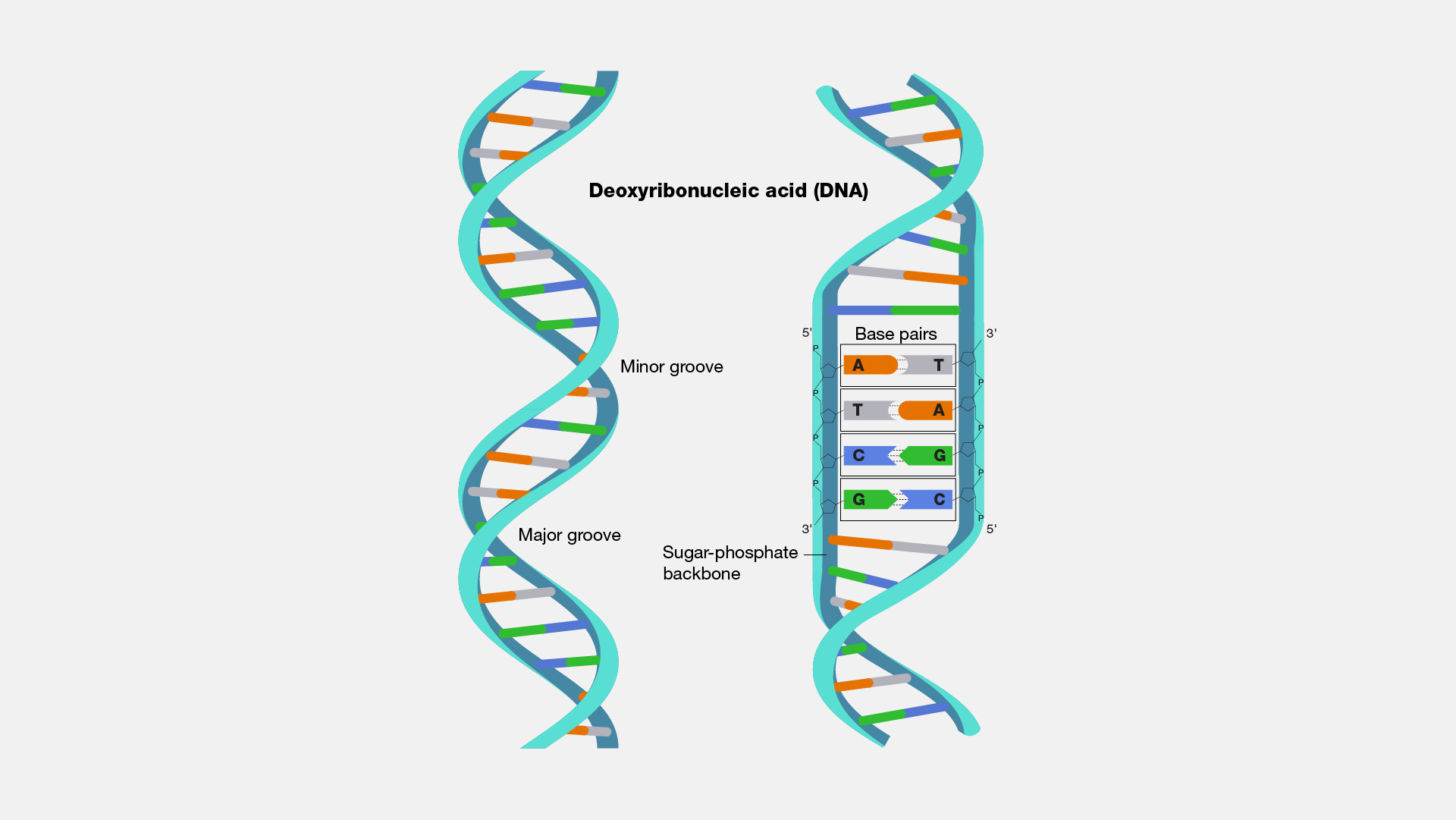
Within each cell is a long, thread-like molecule called DNA that contains genetic information. Prokaryotic cells' cytoplasm contains DNA, but eukaryotic cells' nuclei contain chromosomes. Viruses have a capsid, or protein coat, covering their DNA. DNA is made up of single units termed nucleosides and nucleotides, which are the structural building blocks of the molecule. Nucleosides are generated when a nitrogen base, deoxyribose sugar, and phosphate ion combine to form a single unit. Different people have distinct nucleotide sequences. Thus, they also differ in terms of attributes. Two antiparallel strands make up DNA. DNA has four different forms of nitrogen bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. Although guanine forms a triple bond with cytosine, adenine forms a double bond with thymine. An organism's DNA carries characters or genetic information. A gene is a little section of DNA that codes for a specific trait unique to an organism. Within a chromosome, there are millions of such genes. Characters are passed down from one generation to the next thanks to the DNA that is transferred from mother cells to daughter cells during cell division. DNA undergoes transcription to produce RNA, which aids in protein synthesis.
Ribonucleic acid (RNA)
Each nucleotide in RNA is a polynucleotide that is created by combining a phosphate, ribose sugar, and nitrogen base. Single-stranded RNA exists. It is mostly located in the cytoplasm and is partially present in chromosomes. In viruses, RNA is contained within a capsid. It acts as their genetic material. RNA has four different forms of nitrogen bases: adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil. Whereas guanine has a triple bond with cytosine, adenine has a double bond with uracil. Messenger RNA (mRNA), transfer RNA (t-RNA), and ribosomal RNA (rRNA) are the three different forms of RNA. The synthesis of proteins is RNA's primary job.
Things to remember
- DNA is a long, thread-like molecule within cells that contains genetic information.
- DNA is transferred from mother cells to daughter cells during cell division, and it undergoes transcription to produce RNA, which aids in protein synthesis.
- RNA is a polynucleotide created by combining phosphate, ribose sugar, and nitrogen.
© 2021 Saralmind. All Rights Reserved.


 Login with google
Login with google