Male Reproductive System
Subject: Midwifery I (Theory)

Overview
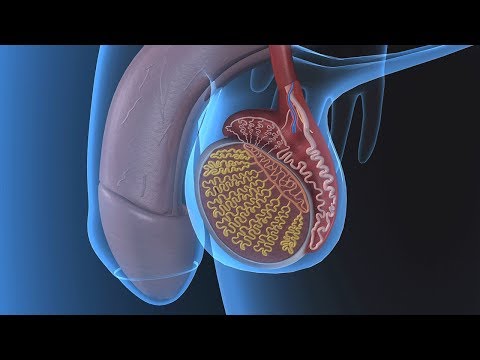
The testes, epididymis, vas deferens, spermatic cords, seminal vesicles, ejaculatory duct, and prostate gland are all internal reproductive organs in men. Furthermore, the scrotum and penis are the exterior reproductive organs. The testes, or male reproductive organs, are housed in the scrotum, one in each sac. The epididymis transports sperm from the testicles to the vas deferens, where it develops and matures before being discharged during ejaculation. A vas deferens connects the epididymis to the ejaculatory duct in each testicle. The spermatic cord travels through the inguinal canal. The deep inguinal ring reveals a variety of structures within the cord. This device holds the testicles in place in the scrotum. The seminal vesicles, which account for around 30% of the semen, create a fluid. The prostate gland secretes around 60% of a man's sperm supply. This discharge is alkaline, which causes sperm to die, and it also contains the enzyme acid phosphatase.
Internal
- Testes
- Epididymis
- Deferent ducts (vas deferens)
- Spermatic cords
- Seminal vesicles
- Ejaculatory duct
- Prostate gland
- Penis
Testes
- It refers to the male sex glands.
- Each compartment in the scrotum contains one testis.
- Functions
- Spermatozoa are formed by seminiferous tubules.
- Interstitial cells secrete testosterone, the main androgen; they increase protein synthesis and promote the development of secondary sex characteristics.
Epididymis
- It transports sperm from the testes to the vas deferens and develops it before ejaculation.
Vas Deferens
- It transports sperm and fluid from the epididymis to the ejaculatory duct.
Spermatic Cords
- The inguinal canal houses the spermatic cord. The components within the cord diverge at the deep inguinal ring. It keeps the testes suspended in the scrotum.
Seminal Vesicles
- It secretes fluid that accounts for approximately 30% of sperm.
Ejaculatory Duct
- Inject sperm into the urethra.
Prostate Gland
- Secretes approximately 60% of sperm; secretion is alkaline, which increases sperm mortality; contains acid phosphatase enzymes
External
- Scrotum
- penis
Scrotum
- It contains the testes, epididymis, and the early section of the seminal ducts; sperm grows at a temperature 2 to 3 degrees below body temperature.
Penis
- It contains the urethra and vascular spaces that, when filled with blood, generate an erection.
REFERENCE
Chaudhari B.D., 1996, Handbook of General anatomy, 3rd edition CBS Publisher and distributors
Chaudhari B.D., 1998, Human Anatomy (Vol. 1, 2, 3), 3rd edition CBS Publisher and distributors
Pathak T., 2057, A handbook of Anatomy and Physiology, 3rd edition, Vidhyarthi Pustak Bhandar, Bhotahiti, Kathmandu
Tuladhar K., Shrestha U., Henk C., 1992, Integrated science, First Edition, HLMC
Tuitui R., suwal, S.N. 2001, Human anatomy and physiology, first edition, Makalu Books and stationers, Putalisadak, Kathmandu
Tuitui R. 2002, A textbook of Midwifery A (Antenatal), 3rd edition, Vidyarthi Pustak Bhandari (Publisher and Distributor), Bhotahity, Kathmandu
Things to remember
- The internal male reproductive system, which includes the testes, epididymis, vas deferens, spermatic cords, seminal vesicles, ejaculatory duct, and prostate gland, is in charge of fertilization and sperm generation.
- External genitalia include the scrotum and penis. The testes, or male reproductive organs, are housed in the scrotum, one in each sac.
- The epididymis transports sperm from the testicles to the vas deferens, where it develops and matures before being discharged during ejaculation.
- The vas deferens connects the epididymis to the ejaculatory duct in each testicle.
- The spermatic cord travels through the inguinal canal. The deep inguinal ring reveals a variety of structures within the cord. This device holds the testicles in place in the scrotum.
- The seminal vesicles, which account for around 30% of the semen, create a fluid.
- The prostate gland secretes around 60% of a man's sperm supply. This discharge is alkaline, which causes sperm to die, and it also contains the enzyme acid phosphatase.
Videos for Male Reproductive System
Questions and Answers
Explain the internal and external male reproductive organ.
Internal:
- Testes
- Epididymis
- Deferent ducts (vas deferens)
- Spermatic cords
- Seminal vesicles
- Ejaculatory duct
- Prostate gland
- Penis
Testes:
- It is a man's sex organs.
- One testis is present in each compartment of the scrotum.
- Functions
- Spermatozoa are formed by seminiferous tubules.
- Interstitial cells secrete the major androgen, testosterone, which increases protein synthesis and promotes the development of secondary sex characteristics.
Epididymis: It transports the sperm-maturing semen from the testes to the vas deferens for storage prior to ejaculation.
Vas deferens Transports sperm and fluid from every epididymis to a duct that produces sperm.
Spermatic cords: The inguinal canal accommodates the spermatic cord. The internal cord structures diverge at the deep inguinal ring. The testes are kept suspended in the scrotum.
Seminal vesicles: It releases fluid, which accounts for around 30% of semen.
Ejaculatory duct: The urethra after ejaculating semen
Prostate gland: Contains the enzymes acid phosphatase and secretes around 60% of the semen, which is alkaline and promotes the mortality of the sperm.
External
- Scrotum
- Penis
Scrotum: Sperm grows at a temperature of 2 to 3 degrees below body temperature; it contains the testes, epididymis, and the first portion of the seminal ducts.
Penis: Contains the urethra and blood-filled vascular areas that lead to an erection.
© 2021 Saralmind. All Rights Reserved.

 Login with google
Login with google