Gestational Hypertension
Subject: Midwifery I (Theory)

Overview
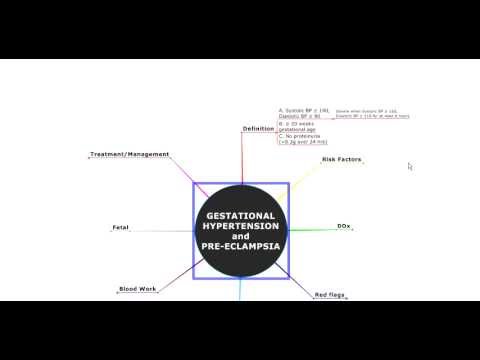
Gestational hypertension is defined as a persistent rise in blood pressure to 140/90 mmHg or higher at least two times 4 or more hours apart after the 20th week of pregnancy or during the first 24 hours following delivery in a previously normotensive woman. It must meet three criteria: there must be no evidence of the underlying cause of hypertension, it must be unrelated to other signs of pre-eclampsia, edema, or proteinuria, and the blood pressure should return to normal within 10 days of delivery.
Gestational hypertension is defined as the development of new hypertension (blood pressure 140/90mmHg) in a pregnant woman after 20 weeks of gestation without the presence of proteinuria or other pre-eclampsia symptoms. Pregnancy Induced Hypertension is another name for it.
Causes
- Having high blood pressure prior to or during pregnancy.
- Pregnancies in multiples
- Being afflicted with renal illness
- Being diabetic
Risk Factors
- Obesity
- Age 35 years or more
- Past history of diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and renal disease
- Adolescent pregnancy
- New paternity
- Multiple gestations
- Placental abnormalities
- Family history of eclampsia
Signs and Symptoms
- Severe headache
- Excessive vomiting
- Blood vomiting
- Dizziness, Drowsiness
- Fever
- Double vision
- Sudden blindness
- Abdomen pain
- Blood in urine
- Excessive swelling of feet and hands.
Diagnosis and Tests
- Urine tests for the presence of protein
- Blood clotting test
- Blood pressure monitoring
- Check for any swelling and weight of the material
- Liver Function Test
- Kidney Function Test
Prevention and Treatment
- Maintain accurate records of the mother's blood pressure.
- Maintain fetal status monitoring with a Doppler and fetal kick count.
- Encourage a nutritious and well-balanced diet.
- Regular physical activity.
- Consumption of salt to taste
- Water and other liquid diets should be consumed in large quantities.
- Increased protein intake while decreasing fried and junk food consumption.
- Elevate your feet numerous times throughout the day and avoid alcohol and coffee-containing beverages.
- Regular prenatal visits are recommended.
- Carry out the necessary lab tests and investigations.
- Take the necessary medication as prescribed by your doctor.
Complication
- Placental abruption
- Poor fetal growth
- Stillbirth
- Seizures
- Death of both mother and baby
References
- BabyCenter. November 2016. https://www.babycenter.com/0_gestational-hypertension-pregnancy-induced-hypertension_1427402.bc
- Medscape. 1994. 2017 http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/261435-overview
- Web MD. 2005. 2017 http://www.webmd.com/baby/potential-complication-gestational-hypertension#1
- Tuitui R. 2002, A textbook of Midwifery A (Antenatal), 3rd edition, Vidyarthi Pustak Bhandari (Publisher and Distributor), Bhotahity, Kathmandu
- Tuitui R. 2002, A textbook of Midwifery C (Antenatal), 3rd edition, Vidyarthi Pustak Bhandari (Publisher and Distributor), Bhotahity, Kathmandu
- Premed. 19 August 2013. http://www.pregmed.org/pregnancy-induced-hypertension-gestational-hypertension.htm
Things to remember
- Pregnancy Induced Hypertension is another name for it.
- Examine the maternal edema and weight.
- Increased protein intake while decreasing fried and junk food consumption.
- Avoid consuming alcohol and coffee-containing beverages.
Questions and Answers
Define Gestational hypertension.
Gestational hypertension is the development of new hypertension (blood pressure 140/90mmHg) in a pregnant woman after 20weeks of gestation without a presence of proteinuria, or other signs of pre- eclampsia. Pregnancy Induced Hypertension is another name for it.
Define gestational hypertension. Explain its causes, symptoms, and management.
Gestational Hypertension
The development of new hypertension (blood pressure of 140/90 mmHg) in a pregnant woman after 20 weeks of gestation without the presence of proteinuria or other indications of pre-eclampsia is known as gestational hypertension. A different name for it is pregnancy-induced hypertension.
Causes
- Prior to becoming pregnant or when previously pregnant, having high blood pressure.
- A number of pregnancies
- A kidney condition
- Being a diabetic
Risk Factors
- Obesity 35 years of age or older
- Diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and kidney illness in the past
- Teenage pregnancy
- A fresh paternity
- Multiple pregnancies
- Anomalies in the womb
- Eclampsia in the family history
Signs and Symptoms
- Terrible headache
- A lot of vomiting
- Violent vomiting
- Drowsiness and vertigo
- Fever
- Dual perception
- Abrupt blindness
- Stomach ache
- Excessive hand and foot swelling blood in the urine
Diagnosis and Tests
- Tests for the presence of protein in urine
- Test for blood clotting
- Monitoring blood pressure
- Check the maternal Liver Function Test for any edema and weight changes.
- Test for Kidney Function
Prevention and Treatment
- Keep track of the mother's blood pressure and make the necessary records.
- Continually check the fetal status with a Doppler and a fetal kick counter.
- Encourage a nutritious, well-balanced diet
- Exercising frequently.
- Consuming salt according to taste
- Drink a lot of liquids, such as water and other diets.
- Lowered the number of junk food and fried meals while increasing the protein consumption.
- Elevate your feet numerous times throughout the day, and stay away from alcoholic and coffee-containing drinks.
- Visit for routine prenatal examinations.
- Carry out the necessary lab tests and research
- Take the necessary medication as directed by a doctor.
Complication
- Abrupt placentation
- Faulty fetal growth
- Stillbirth
- Seizures
- Mother and child both pass away
Define gestational hypertension. Explain its causes, symptoms, and management.
Gestational hypertension
The development of new hypertension (blood pressure of 140/90 mmHg) in a pregnant woman after 20 weeks of gestation without the presence of proteinuria or other indications of pre-eclampsia is known as gestational hypertension. A different name for it is pregnancy-induced hypertension.
Causes
- Prior to becoming pregnant or while previously pregnant, having high blood pressure.
- A number of pregnancies
- A kidney condition
- Being a diabetic
Risk factors
- Obesity
- 35 years of age or older
- Diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and kidney illness in the past
- Teenage pregnancy
- A fresh paternity
- Multiple pregnancies
- Anomalies in the womb
- Eclampsia in the family history
Signs and symptoms
- Terrible headache
- A lot of vomiting
- Violent vomiting
- Drowsiness and vertigo
- Fever
- Dual perception
- Abrupt blindness
- Stomach ache
- Excessive hand and foot swelling blood in the urine
Diagnosis and Tests
- Tests for the presence of protein in urine
- Test for blood clotting
- Monitoring blood pressure
- Check the maternal Liver Function Test for any swelling and weight changes.
- Test for Kidney Function
Prevention and treatment
- Keep track of the mother's blood pressure and make the necessary records.
- Continually check the fetal status with a Doppler and a fetal kick counter.
- Encourage a nutritious, well-balanced diet
- Exercising frequently.
- Consuming salt according to taste
- Drink a lot of liquids, such as water and other diets.
- Lowered the number of junk food and fried meals while increasing the protein consumption.
- Elevate your feet numerous times throughout the day, and stay away from alcoholic and coffee-containing drinks.
- Visit for routine prenatal examinations.
- Carry out the necessary lab tests and research
- Take the appropriate medication as directed by a doctor.
Complication
- Abrupt placentation
- Faulty fetal growth
- Stillbirth
- Seizures
- Mother and child both pass away
© 2021 Saralmind. All Rights Reserved.

 Login with google
Login with google