Virginia Henderson's Nursing Need theory
Subject: Fundamentals of Nursing

Overview
Virginia Henderson's Nursing Need Theory
Virginia A. Henderson created the "Nursing Need Theory" to describe the special emphasis of nursing practice. This theory focuses on the fundamental needs of people and how nurses may help to address those needs. Henderson contends that everyone has requirements that are fundamental to their health. They might need help getting healthy and independent or getting help dying peacefully. In order to help the patient become as independent as possible, she described the nurse's role as substitutive (doing for the person), supplementary (helping the person), and complementary (working with the person).
Henderson's needs theory is relevant to several nursing specialties with a range of practice areas. It is extremely flexible to use this theory in practice, and doing so enables one to assess their nursing competency when it comes to preserving a person's degree of independence and health promotion. Based on human needs, she divided nursing tasks into 14 components. The Need Theory's 14 parts demonstrate a wholistic approach to nursing that addresses the needs of the body, mind, spirit, and society. Nine of the first 10 parts are physiological. Communication and learning psychology is discussed in the tenth and fourteenth points. The eleventh element is moral and spiritual. The thirteenth and fourteenth components are sociologically focused on work and leisure.
Henderson's 14 Components as Applied to Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
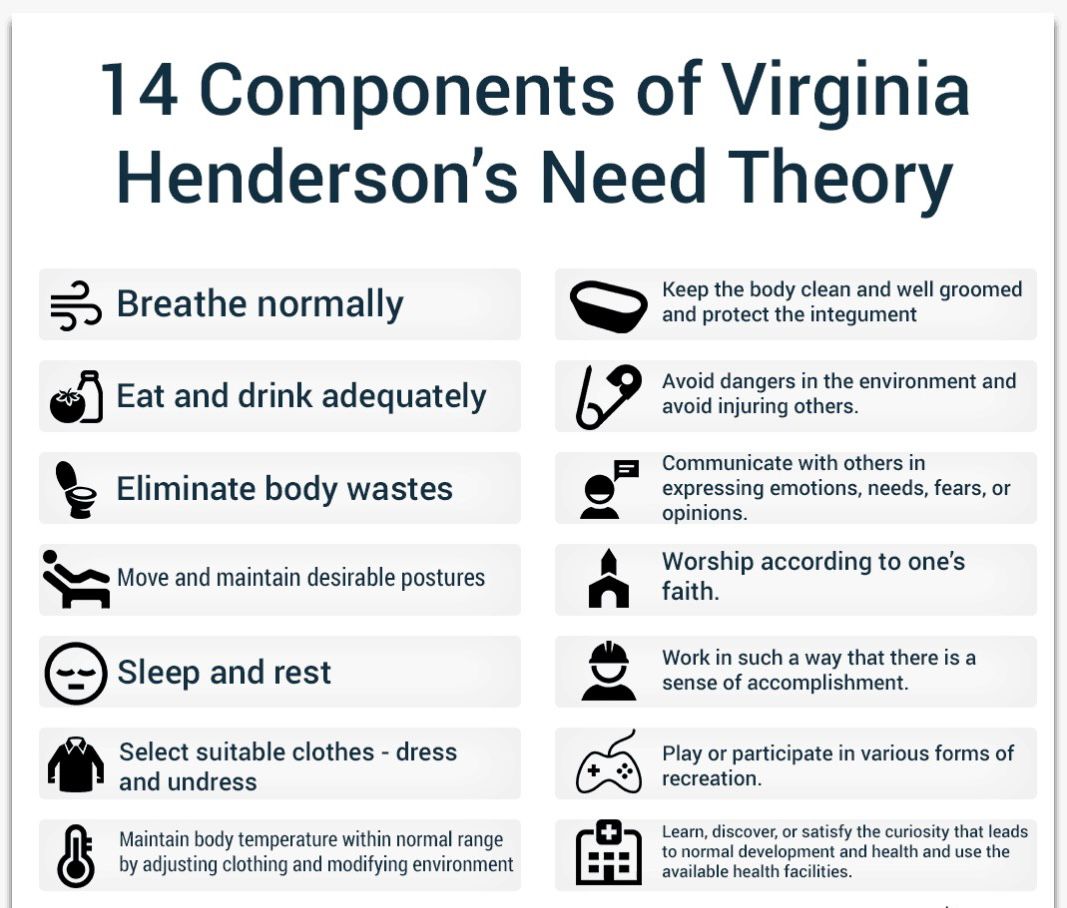
Henderson's 14 components can be used or compared to Abraham Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs due to their many similarities. Maslow's physiological needs cover components 1 through 8, while safety needs include component 9. The Love and Belongingness category includes the tenth and eleventh component, whereas the self-esteem requirements category includes the twelveth, thirteenth, and fourteenth component.

Things to remember
© 2021 Saralmind. All Rights Reserved.

 Login with google
Login with google