Skin Care
Subject: Fundamentals of Nursing

Overview
Skin Care
The skin is the body's outermost layer of protection. On the skin's surface, perspiration and sebum are secreted by sebaceous glands, respectively. If these fluids build up too much, germs and dust will start to gather. In addition, the development of debris and body odor is caused by worn-out epithelial cells on the skin's surface. To avoid or eliminate unpleasant odors and dirt from the skin, regular bathing is necessary.
Nursing care is not complete without bathing the patients. The nurse is still in charge of making sure the client's hygiene needs are addressed, whether she gives the client a bath herself or assigns the task to another medical professional. Depending on a person's cultural norms, kind of disease, skin condition (dry skin demands fewer baths), type of weather, etc., the frequency of bathing may vary.
Purposes
- body of the customer to be cleaned.
- to encourage blood flow.
- Tt revitalize the patient
- to encourage rest and sleep.
- to stop germs from spreading over skin.
- to enhance the patient's sense of self.
- help enhance joint and overall muscle tone.
- to avoid bed sores.
- in order to lower body temperature.
- to give the patient and family the chance to learn ideal personal hygiene.
Principles
- Cover the sick to provide them comfort and seclusion.
- Before and after the treatment, proper hand cleaning is crucial.
- It is important to preserve the body mechanics principle.
- Healthy, intact skin serves as a barrier against dangerous substances.
- Ensure security and stop falls.
- The frequency of baths depends on the state of the skin.
- Do not wash lacerated skin with soap.
- To find bed sore early warning signals, skin and back examination is required.
- Bony prominences that fold and wrinkle need extra care because they are more likely to develop bed sores.
- For adults, the recommended water temperature is 110–115°F (43–45°C), and for youngsters, 100–105°F.
- Always clean the body parts in order of cleanliness, exposing one portion of the body at a time to be washed, rinsed, and dried.
- To avoid back pain, apply creams or oils.
- Never put spirit directly on your skin.
- While doing the treatment, give active and passive exercise and health guidelines.
Types of Bath
Baths are generally categorized into two types:
- Cleaning bath.
- Therapeutic bath.
Cleaning Bath
Cleaning bath is provided as routine client care. The main purpose of cleaning bath is maintenance of personal hygiene. We can categorize this type of bath in the following ways:
- Bathroom bath (Shower/Tub bath).
- Complete bed bath (sponge bath).
- Partial bath.
Bathroom Bath (Shower bath/Tub bath)
Ambulatory patients may be allowed to take a bath in the bathroom with some assistance from the nurse.
Articles
- Soap with dish.
- Towel.
- Warm tap water.
- Clean clothes-1 set.
Procedures
| S.N. | Nursing Action | Rationale |
| 1 | Identify the patient and any specific instructions. | Ensures that right procedure is performed for right patient. |
| 2 | Assess the patients for bathing need, condition of the skin, activity tolerance, range of motions of extremities and bathing preference. | Provides information about patient. |
| 3 | Explain the patient and his relatives about the procedure. |
Reduces anxiety and encourage cooperation. |
| 4 |
Wash hands. Collect the articles. |
Facilitates to perform procedure. |
| 5 |
Observe that the bathroom floor is not slippery and is warm. Assist the patient up to the bathroom (if needed). |
Prevents from falling |
| 6 | Maintain privacy by closing the bathroom door. | Reduce patient's embarrassment. |
| 7 |
Keep the bathroom door unlocked so that in case of needs the nurse or other health personnel can enter. |
Promote safety. |
| 8 | Assist the patient in bathing as needed. | Promotes comfort |
| 9 |
Help him to go to bed as needed. Help the patient in dressing. Comb hair, protecting the bed with a towel. Make the bed tidy or change the linen as needed. |
|
| 10 | Keep the patient in comfortable position. | |
| 11 | Take vital signs. | Determines the patient's condition. |
| 12 |
Clean and replace all articles. Wash hands. |
Leaves the unit clean and articles ready for further use. |
| 13 | Give health education to the patient and relatives on skin care. | Provides necessary information. |
| 14 | Record and report the procedure. | Provides accurate documentation. |
Complete Bed Bath
Cleaning a dependent patient's complete body while they are in bed is referred to as a bed bath, sponge bath, or bed cleaning. There are many levels of bed bathing. Complete bed bathing entails cleansing all skin regions, such as the face, hands, axilla, groin, perineal area, feet, etc., where dirt or secretions tend to gather.
Indications
- Patients that are unconscious or partially awake.
- Patients in beds.
- patients with paralysis.
- Orthopedic patient with traction and a plaster cast.
- Patients who are gravely unwell.
Articles
- Bowl-2,
- Big bucket - 2 (one for warm water and the other is for collection for dirty water),
- Jug,
- Bucket for waste,
- Sponge clothes - 3,
- Soap with dish.
- Clean cloth (gown),
- Mackintosh -1,
- Towels - 2,
- Gauge piece/cotton balls -some amount,
- Bath thermometer -1 if available,
- Bath blanket/ sheet -1,
- Oil or lotion.
- Cap,
- Nail cutter,
- Body powder,
- Trolley.
Procedure
| S.N. | Nursing Action | Rationale |
| 1 | Identify the patient/Check client's identification. | Ensures that right procedure is performed for right patient. |
| 2 | Assess the patients for bathing need, condition of the skin, activity tolerance, range of motions of extremities and bathing preference. | Provides information about patient. In some instance a bed bath may be harmful for a client. |
| 3 |
Explain the procedure to the patient if he/she is oriented and relatives. Encourage participation from the patient or the relatives. Close windows and doors to make sure that the room is free from drafts and switch off fan. |
Reduce anxiety and encourage cooperation. Air currents increase loss of heat from the body. |
| 4 | Provide privacy by drawing curtains and closing doors or Screen the patient. |
Reduce patient's embarrassment. |
| 5 | Offer bedpan or urinal if he or she requires | Enhances comfort of the patient. |
| 6 |
Prepare bed and position the patient appropriately. Place bed in a high position. Position the patient (supine position) close to the right side of the bed or close to the nurse. |
Reduces strain to the nurse's back. |
| 7 |
Prepare hot water. Fill two basins about two thirds full with warm water (110, 115F). Check temperature of water by pouring water on the inner aspect of the palm. |
Provides warmth to the patient. Prevents risk of burn. |
| 8 | Remove patient's clothing and cover the client's body with a bath blanket or sheet. Expose only that part of the body which is to be washed. | Ensures privacy and prevents chills for the patient. |
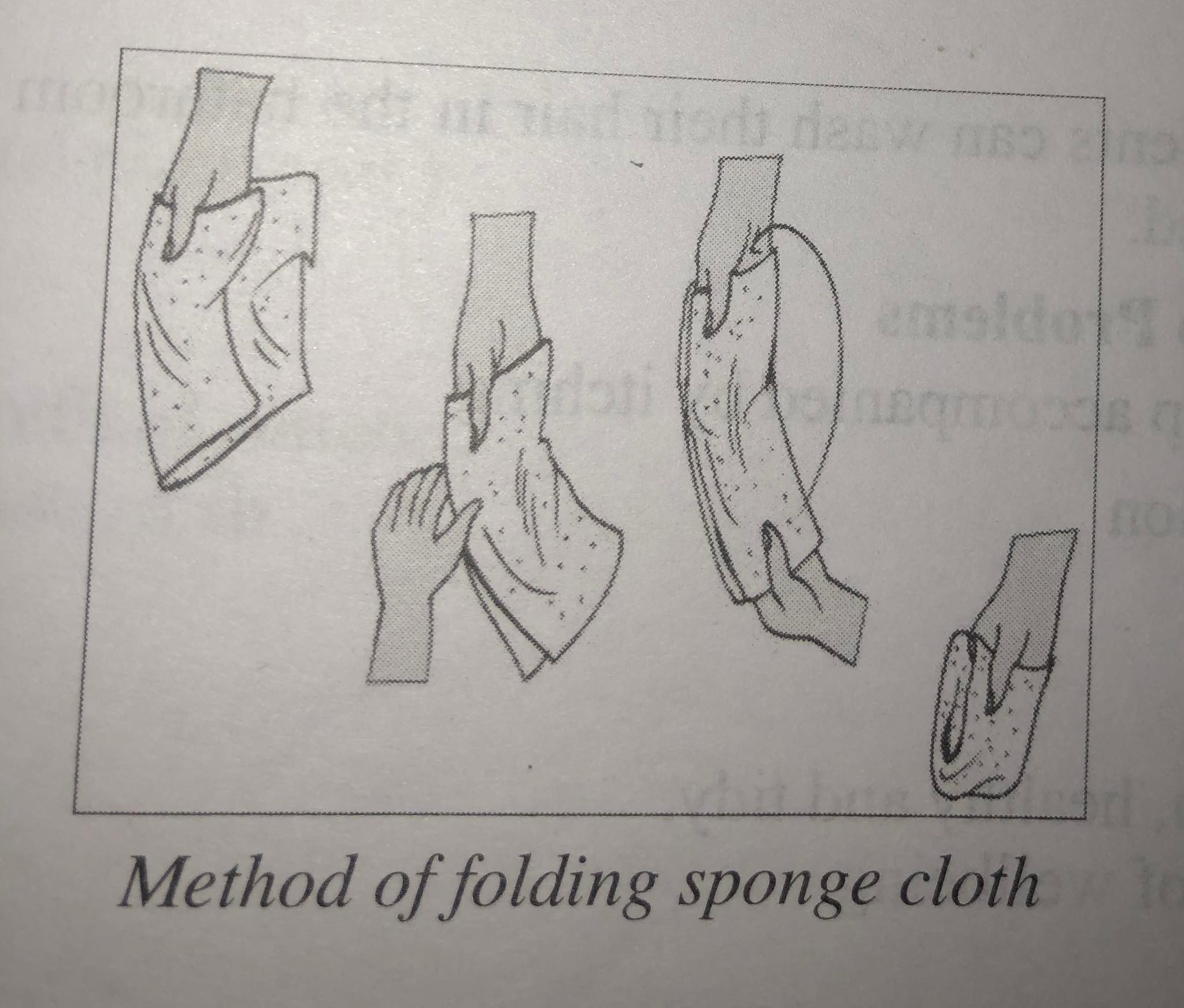
| 9 | Make mitts with the wash cloth. | Mitts conserve heat of the water and prevents tip of wash cloth from trailing and dripping over patient's body. |
| 10 |
Wash face and neck
|
Prevents wetting of pillows and bed linen. Bath mitt retains temperature of water. Prevents transmission of organisms from one eye to another, wiping from inner to outer canthus prevents secretions from entering nasolacrinal duct. Soap if remaining on skin will cause irritation.
|
| 11 |
Wash chest and abdomen
|
Prevents unnecessary exposure of patient. Protects bed linen from becoming wet. |
| 12 |
Wash arms and hands
|
Protects bed linen from becoming wet. Washing the far side first prevents dripping bath water onto a clean area. Long strokes improve circulation be facilitate venous return. Excessive rubbing may cause skin injuries. |
| 13 | Wash lower extremities.
|
Moving from distal to proximal improves venus circulation and removes dirt from skin pores. |
| 14 |
Wash the back of patient
|
Provide clear visualization and and expose the back. |
| 15 | Encourage the patient to clean the perineal area if he/she is able to do so. Otherwise request the patient's visitor or the nurse should do for the patient. | Encourage patient's independence. |
| 16 | Apply moisturize or body lotion if the patient prefers or if skin is dry. | Lotions prevent drying and chapped skin. |
| 17 | Help the patient in dressing. Comb hair, protecting the bed with a towel. | Provide warmth and comfort. |
| 18 | Make the bed tidy. Change the bed linen. Remove screen. | Promote comfort. |
| 19 | Position the patient in a comfortable manner. | |
| 20 | Take vital signs. | Determines the patient's condition. |
| 21 |
Wash, dry and return the articles to proper place. Wash hands. |
Leaves the unit clean and articles ready for further use. |
| 22 | Document on the patient chart including date, time and patient's condition. Report findings if any to the senior staff. | Proper documentation provides coordination of care. |
Key Points
- Before starting the process, take care of your mouth.
- Before taking a bath, empty the bladder.
- When the water gets chilly or filthy, replace it.
- Inform the patient's family about the value of taking a bath for their health.
- Obtain aid if necessary if the patient is defenseless or unconscious.
- In order to guarantee proper body mechanics, the nurse may switch from one side of the bed to the other if the patient is fat or unable to move in bed.
- Before giving a patient a bath, evaluate their general health. Do not give a bath if you are unstable.
- Given just after eating, a bath should be avoided since it interferes with digestion.
Things to remember
© 2021 Saralmind. All Rights Reserved.

 Login with google
Login with google