Plantae Kingdom
Subject: Science

Overview
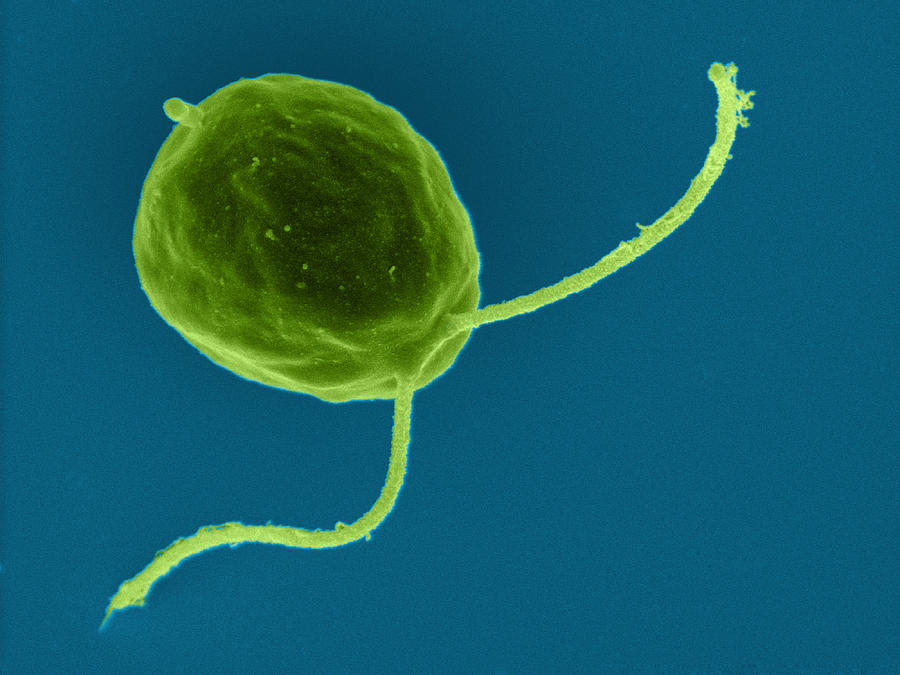
Chlorophyll is a green pigment found in various plants, including Chlamydomonas bacteria, moss, fern, pine, pea, and maize. These plants belong to the kingdom Plantae and are divided into three groups: algae, bryophyta, and trachaeophyta. Algae plants are single- or multicellular autotrophs and feed on themselves. Bryophyta plants are more developed and found in moist, shaded areas. Tracheophyta plants have distinct parts of the plant body, with vascular tissue responsible for carrying substances.
Let's observe and think:
|
Moss |
Fern |
Pea |
Maize |
Pinus |
- Which organisms in the image are comparable to one another?
- To what kingdom are they affiliated?
- What characterizes the kingdom to which they belong?
- What distinguishes ferns from mosses?
Chlorophyll is a green pigment found in the bodies of Chlamydomonas bacteria, moss, fern, pine, pea, and maize. They are a member of the kingdom Plantae, which also includes multicellular and unicellular green plants. Cellulose makes up their cell wall. They feed on themselves. There are plants that flower and those that don't. These plants are divided into three groups according to their structural makeup: algae, bryophyta, and trachaeophyta.
Algae
|
Spirogyra |
Volvox |
Fucus |
It is impossible to distinguish between the root stem and leaf of the plants in the image, such as the Spidergyra, Volvox, Fucus, etc. The thallus is their plant's main body. They have cell walls and chlorophyll in their cells. These are divisional algae plants. The following traits apply to the plants in this division:
- They can be single- or multicellular.
- Because they have chlorophyll, they are autotrophs. They use starch to prepare and preserve food.
- Cellulose makes up their cell wall.
- They procreate via both asexual and sexual means.
- Ponds, rivers, the sea, and marshy areas are home to these plants.
For instance, Fucus, Ulothrix, Spirogyra, Volvox, and Chlamydomonas.
Bryophyta
|
Marchantia |
Moss |
Riccia |
Compared to algae, plants like the Marchantia, moss, and riccia in the image are more developed. These plants are verdant. The thallus makes up the plant body of Marchantia, whereas the rhizoid, stem, and simple leaf make up the plant body of moss. These plants are found in moist and shady places. Plants in bryophyta need water for fertilization. So, they are also called amphibian plants. The general characteristics of plants under bryophyta are as follows:
- These are plants with many cells.
- They feed on themselves.
- The plant body is either a thallus or it can differentiate into a simple leaf, stem, and rhizoid.
- They can be found in damp, shaded areas.
- The gametophyte plant body is that of these dioecious plants. In Antheridium, male plants produce male gametes. In archegonium, female plants generate female gametes. This stage is therefore known as the gametophyte. After emerging from the antheridium, the male gamete travels by water to the archegonium, where it unites with the ovum to produce a zygote. After that, the zygote germinates and becomes an asphorophyte. The spore mother cell divides through meiosis during this phase to produce haploid spores. Because spores are formed here, this phase is known as the sporophyte phase.
- Alternation of generation is the process by which sporophytic and gametophytic generations follow one another to finish a plant's life cycle. In these plants' life cycle, the gametophytic generation is dominant and independent.
- There is no vascular tissue in them. They spread out and attach themselves to a substrate, or they develop to a height of only a few tiny centimeters.
For instance, moss, Marchantia, Riccia, etc.
Tracheophyta
|
Fern |
Cycas |
Banana |
The base, stem, and leaf of the fern, Cycas, banana, peepal, etc. that are depicted in the image are distinct parts of the plant body. Their vascular tissue, xylem and phloem, is responsible for carrying substances throughout the body.
Therefore, the division tracheophyta includes these plants. Splitting. The tracheophyta group of plants comprises dwarf herbs, shrubs, large, mature plants, and non-flowering ferns. Pteridophyta, Gymnosperm, and Angiosperm are the three subdivisions of the division Tracheophyta based on structure.
A. Pteridophyta
|
Fern |
Horse tail |
Clubmoss |
Plants such as ferns, clubmosses, and horse tails are characterized by their large roots, stems, and leaves; these plants are not flowering. Their leaves resemble feathers. Typically, its stem takes the shape of a rhizome and is buried horizontally beneath the ground. This section includes plants such as fern, fiddlehead fern, ground gooseberry, Lycopodium, Selaginaella, Pteris, etc. The following lists the general traits of the plants that belong to the Pteridophyta subdivision:
- Humid and shaded areas are their habitat.
- They have no seed but plant body is differentiated into roo stem and leaf. Leaf is feather like; stem is under-developed in the form of rhizome and root is developed.
- They have developed vascular tissue like xylem and phloem.
- These plants have a lot of brown dots called sori (plural: sorus) on the underside of their leaves. Sporangium, or sporangia in plural, is the part of the sorus that makes spores. It's possible that some leaves lack sori. Sporophyll is the term for a leaf with sori, whereas tropophyll is the term for a leaf without sori. Because it generates haploid spores, the plant body is known as a sporophyte.
- Spores fall to the ground by the rupture of sporangia, which, given the right conditions, germinate into gametophytes known as prothalli (sing., prothallus). Male and female gametes are produced by gametophytes.
- They also exhibit generational fluctuation in their life cycle. The sporophytic phase is longer-lasting and dominating.
B. Gymnosperm
|
Pinus |
Juniper |
Cycas |
Plants that are kept under blooming plants, such Cycas, Juniper, Pinus, etc., bear cones rather than flowers. Their seeds are bare and devoid of fruit. The traits of the plants are as follows:
- Gymnosperms are the earliest plants to develop seeds in the course of plant evolution.
- Rather than flowers, they bear cones. Cones are male and female specific. They are hence monosexual. Wind is the means of pollination.
- Since the cone lacks an ovary, no fruits are produced. The seed is nude.
- They have needle-like, elongated leaves. e. Thick bark encloses the stem.
- These plants are referred to as coniferous plants because of their inverted cone-like shape.
- These plants have extensive underground roots.
Example: Cycas, Pinus, Juniper, Himalayan yew, Himalayan cedar
C. Angiosperm
|
Bamboo |
Soyabean |
True flowering plants include soybeans, bamboo, and other plants. Fruit has seeds inside of it. Thus, these plants fall under the angiosperm subdivision. The following list includes general traits of plants retained in angiosperms:
- They are the kingdom Plantae's most evolved plants.
- Both on land and in water, these plants are ubiquitous.
- Their fruit, flower, stem, root, and leaf are all fully formed.
- They produce actual flowers that have both ovules and ovary inside of them.
- While certain plants are unisexual, others are bisexual.
- A variety of mediums, including the wind, water, insects, and animals, are used in pollination.
- The fruit on these plants contains seeds.
This subdivision includes things like oranges, maize, bananas, rice, soybeans, water hyacinth, Lemna, Pistia, etc.
Angiosperms are divided into two classes: monocotyledon and dicotyledon, based on the number of cotyledons found in their seeds.
a. Monocotyledon
The plants depicted in the image have thin, elongated leaves. The veins are parallel to one another. Every plant has identical roots that grow from the same spot. So these plants an kept in the monocotyledon class. General characteristics of plant under this class are mentioned below:
- The leaves exhibit parallel veining.
- Their roots are fibrous.
- Their stems are typically hollow. Nodes are evenly spaced and noticeable. Branches and leaves emerge from the node. The base of the leaf spreads out to encase the stem in a sheath.
- Dispersed throughout the stem are xylem and phloem, which are vascular tissues.
- The number of floral parts is three or multiples of three.
- The fruit has seeds inside of it. All that is present in seeds is the cotyledon.
- They can be found in both water and land. This class includes things like barley, bamboo, sugarcane, bananas and wheat.
b. Dicotyledon
Broad, flat leaves are characteristic of the plants in the image, including the mustard, pea, orange, soybean, and bean. The leaf blade has a midrib, from which numerous veins and veinlets emerge to form a network. They have a noticeable main root that gives rise to smaller branching roots. Two cotyledons are present in their seeds. They are thus assigned to the dicotyledon class. The traits of dicotyledonous plants are as follows:
- These plants vary greatly in size, from little shrubs to enormous trees.
- Their system is taproot.
- The stem is primarily woody, sturdy, and robust. There are nodes everywhere at random times.
- Inside the stem, vascular bundles are organized in a ring-like pattern.
- The leaf contains reticular veins. The leaf can be simple or complex, and the stem is petiolated.
- Fruit contains seeds inside of it. There are two cotyledons on a seed. This class includes, among others, beans, pumpkin, oranges, mangoes, mustard, peas, and soybeans.
Things to remember
- These plants are divided into three groups according to their structural makeup: algae, bryophyta, and trachaeophyta.
- Pteridophyta, Gymnosperm, and Angiosperm are the three subdivisions of the division Tracheophyta based on structure.
- Angiosperms are divided into two classes: monocotyledon and dicotyledon, based on the number of cotyledons found in their seeds.
© 2021 Saralmind. All Rights Reserved.







 Login with google
Login with google