Climate
Subject: Science

Overview
Climate change refers to the long-term average of weather patterns over a period of time, usually 30 years or more. It is a major global issue, particularly affecting developing nations like Nepal. Communities that rely on natural resources are more vulnerable to the effects of climate change, which is a result of both natural and human-caused factors. Nepal is particularly vulnerable to the negative consequences of climate change, as its annual temperature has been rising at a rate of 0.06°C. Climate change has significantly impacted Nepal's Himalayan range, glaciers, and ecosystems, leading to increased rainfall, drought, and increased sea levels. Climate change also affects biodiversity, altering the life cycles of marine and terrestrial species and posing risks to human health. To control climate change, the Nepali government has developed policies and initiatives, such as the Environmental Protection Act of 2076. To reduce climate change, measures include reducing carbon emissions, prioritizing carbon storage, and raising public awareness and behavior.
Climate is the long-term average of the weather in a particular geographic area over a period of time, usually thirty years or more. In general, a location's climate doesn't change. The climate of the Earth is not affected by minute natural changes. However, the world's climate has altered as a result of human activity's release of various greenhouse gases. The outcome has been significant changes in the weather patterns in different places.
Climate Change
The impact of climate change is greater in developing nations than in industrialized ones, making it a major worldwide issue. Although Nepal contributes very little to greenhouse gas emissions, the country is very vulnerable to the negative consequences of climate change. Along with the climate's long-term natural fluctuations, direct or indirect human activity-related changes in the atmosphere's composition have also gradually altered Earth's climate.  Climate change is the process of a location's climate changing over an extended period of time as a result of unpredictable natural phenomena and diverse human activity. Climate change disrupts a place's typical weather cycle. In general, a shift in the statistical magnitude of the weather over an extended period of time is referred to as climate change. Researchers from all across the world have examined the consequences of climate change by examining a variety of sources, including meteorological data, satellite photos, and study reports from the areas impacted by the phenomenon. Climate change also affects Nepal. Since then, Nepal's annual temperature has been rising at a pace of 0.06°C. Every year, a number of water sources, including lakes, fountains, and rivers, dry up and their water volume shrinks.The likelihood of flooding from glacial lake eruptions is equal. The melting of snow is causing a decrease in the height of mountains. From all of this information, it is obvious that climate change has a negative impact on Nepal as well.
Climate change is the process of a location's climate changing over an extended period of time as a result of unpredictable natural phenomena and diverse human activity. Climate change disrupts a place's typical weather cycle. In general, a shift in the statistical magnitude of the weather over an extended period of time is referred to as climate change. Researchers from all across the world have examined the consequences of climate change by examining a variety of sources, including meteorological data, satellite photos, and study reports from the areas impacted by the phenomenon. Climate change also affects Nepal. Since then, Nepal's annual temperature has been rising at a pace of 0.06°C. Every year, a number of water sources, including lakes, fountains, and rivers, dry up and their water volume shrinks.The likelihood of flooding from glacial lake eruptions is equal. The melting of snow is causing a decrease in the height of mountains. From all of this information, it is obvious that climate change has a negative impact on Nepal as well.
Causes of Climate Change
Climate change can be attributed to both natural and human-caused forces. The lives of communities that depend on natural resources are thought to be more vulnerable to the effects of climate change because of factors such as poverty, illiteracy, and social inequality. There are two categories of causes of climate change: natural and human-caused.
Natural Cause
A variety of natural events have an impact on the environment. These kinds of natural occurrences lead to the generation of greenhouse gases, which in turn cause climate change. Below are a few examples of natural activities:
- Solar Activities
Thermonuclear fusion processes are responsible for the sun's energy production. The rate of this process varies along with the energy the sun produces. This also has an impact on the amount of solar radiation that reaches the earth's surface. These changes have an impact on the weather. Thus, these fluctuations in solar activity contribute to climate change.
- Change in the Reflectivity of the Earth
The composition of the earth's surface and atmosphere determines how much solar energy is reflected off of them. The planet absorbs around 70% of the solar light that strikes it. It plays a part in the climatic shifts that cause natural alterations on Earth's surface, such as the melting of glaciers. Water vapor, which is produced when water evaporation occurs in rivers, lakes, and other bodies of water, is also considered a greenhouse gas. The rate of evaporation varies in response to variations in the sun's heat and light radiation reaching the surface of the planet.
- Volcanic Eruption
Volcanoes have had a significant impact on the climate. A variety of gases, such as aerosols and carbon dioxide, are released during volcanic eruptions. The earth's surface becomes chilly for a while as a result of these gases and aerosols spreading up into the upper atmosphere and blocking solar energy. Furthermore, in these situations, released greenhouse gases stay in the atmosphere for a very long period, maintaining the earth's warmth.
Human-induced Cause
Climate change is also a result of a variety of human activities. Because of human-caused activities, greenhouse gases are created in large quantities. These gases create a thick layer over the earth's surface and trap solar heat, raising global temperatures. Below are a few causes:
- Production of Greenhouse Gases
Burning fossil fuels like coal, mineral oil, and natural gas produces a huge number of hazardous gases, including greenhouse gases, which are used to generate heat energy and electrical energy. The earth's surface temperature is rising as a result of this process as well.
- Industrialization
There are numerous types of industries that produce cement, steel, electrical devices, plastic clothing, and other materials. These industries run on fossil fuels. Such fuels emit greenhouse gases into the atmosphere as they burn, contributing to climate change.
- Deforestation
Uncontrolled forest clearing occurs while building roads, constructing human settlements, and cultivating land. Deforestation increases the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere by lowering the amount of carbon dioxide that plants utilize to prepare food. This makes global warming worse. The primary location for storing carbon released into the atmosphere is the forest.
- Burning of Fossil Fuels
Fossil fuels power the vast majority of vehicles, including trucks, buses, aircraft, ships, and cars. As these fuels burn, they release dangerous greenhouse gases, mostly carbon dioxide. These gases warm the planet and contaminate the atmosphere in the process.
Effects of Climate Change
The rise in air temperature over the past several decades has had a negative impact on Nepal's Himalayan range and glaciers, as well as the ecosystems that depend on them. These catastrophes have included excessive rainfall, drought, or lack thereof. The earth's temperature is rising, which is causing snow to melt more quickly. As a result, glacial lakes are growing larger and more likely to burst. The adverse effects of global warming have been seen and immediately felt in sectors pertaining to livelihoods, including housing, infrastructure development, human health, energy supplies, forests and biodiversity, and tourism. Annual property losses have also been significant due to climate-related calamities, including landslides, floods, and forest fires. The following is a description of how climate change affects:
- Drought and Floods
Changes in rainfall patterns brought about by climate change increase the likelihood of drought in certain regions and floods in others owing to an abundance of precipitation. Floods and droughts have an impact on agricultural productivity, raising the possibility of a future food crisis.
- Increasing Sea Level
Due to an abundance of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, climate changes result from an increase in atmospheric temperature. We refer to this general increase in Earth's temperature as global warming. Seawater volume also rises as a result of this temperature rise. Additionally, snowmelt brought on by global warming also raises the sea level. As a result, sea levels rise to the top of islands and beaches, devastating wildlife and plant life as well as their habitats and having an impact on nearby towns.
- Effects on Biodiversity
The earth's temperature is rising due to climate change, which alters the life cycles of marine and terrestrial species. Their physiology, growth, and development are all impacted by these changes. Climate change also has an impact on the ability of terrestrial and marine animal and plant species to adapt. This raises the possibility of those creatures going extinct.
- Negative Impact on Human Health
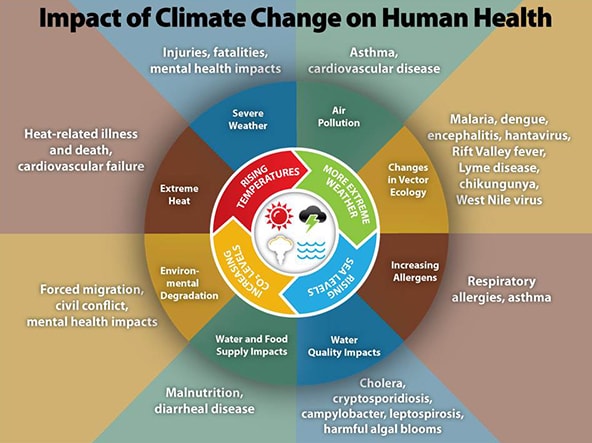
Climate change has a harmful effect on several aspects of the environment. This has an effect on human health as well. It poses a risk to human health by contributing to skin conditions and mental disorders. inadequacies in nutrition, etc.
- Changes in Weather
The weather has changed as a result of climate change. Seasons other than the rainy season get heavy rainfall. Droughts can occur during the rainy season on occasion. Periods of high rainfall, periods of little rainfall, and frequent periods of excessive rainfall all have an impact on agricultural production because crops can survive with little water.
Measures to Control Climate Change
To mitigate the negative consequences and hazards associated with climate change, the Nepali government has developed policies and initiatives. The Environmental Protection Act of 2076 says that the government of Nepal, provincial governments, local governments, and other public bodies, as well as the private sector, can give the orders they need by putting notices in the Nepal Gazette about what needs to be done to lessen the bad effects and risks of climate change. Climate change has a number of detrimental effects on the planet. It is vital to take action to reduce climate change in order to regulate it. The following measurements are listed:
- Reducing Carbon Emission
Excessive carbon emissions are contributing to the increase in global warming. Carbon emissions can be decreased in order to slow down climate change. To achieve this, energy efficiency needs to be raised, and using and conserving energy resources needs to be prioritized. The utilization of renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar power, in transportation should take precedence. This can lower carbon emissions and the use of fossil fuels.
- Emphasizing Carbon Storage
Green plants use carbon dioxide to cook their food and release oxygen into the surrounding air, which is necessary for all living things. Thus, planting and tree conservation should be prioritized in order to preserve forest resources. In this manner, plants are able to store more carbon, reducing the effects of climate change.
- Public Awareness and Change in Behavior
By adopting more ecologically friendly practices, we can reduce the impact of climate change. We should adopt more ecologically friendly practices and work to raise awareness among the general population.
Things to remember
- The process of a place's climate shifting over time due to erratic natural events and a variety of human activities is known as climate change.
- Natural causes include solar activities, changes in Earth's surface and atmosphere composition, volcanic eruptions, and the production of greenhouse gases.
- Human-caused causes include burning fossil fuels, industrialization, deforestation, and burning fossil fuels.
- Climate change also affects biodiversity, altering the life cycles of marine and terrestrial species and posing risks to human health.
- Changes in weather patterns, such as heavy rainfall and droughts, also impact agricultural production.
© 2021 Saralmind. All Rights Reserved.






 Login with google
Login with google