Upthrust
Subject: Science

Overview
The object's weight and the upthrust of the liquid act on it when it is submerged in water or air. The upthrust can either overcome gravity's downward pull or exceed it when pushed down hard into the water. The force of gravity and the upthrust of the liquid are directed in opposite directions, causing the object to sink or rise. The upthrust is pointing upward due to the normal pressure and force on the object's lower surface. The upthrust on an object when submerged in a liquid is determined by the actual weight (W1) and the apparent weight (W2). Factors affecting upthrust include the density of the liquid and the volume of liquid displaced. Archimedes' principle provides the relationship between upthrust and the weight of the displaced fluid.
Let's Observe
Grab an empty plastic bottle and fill a bucket with water. To ensure the bottle is sealed, tighten the cap. Fill the bucket with the bottle.
 On the water, the object floats. Submerge the object in the water and respond to the following inquiries:.
On the water, the object floats. Submerge the object in the water and respond to the following inquiries:.
- Do you sense as though the object is being pushed upward when it is thrown into the water?
- The object falls to the ground when released into the air due to gravity. However, why does it not sink when it is placed on the water's surface? Isn't the bottle affected by gravity when it is submerged in water?
Pushing the object into the water is a challenge. It indicates an upward push on the bottle from the water. The water continues to exert an upward force on the object as it is pushed into the water until the object is fully submerged. The object returns to the water's surface when it is released. Upthrust is the net upward force that water exerts on an object within it. Every fluid exerts upthrust, but the strength of this upthrust varies according to the density of the fluid.
The weight of the object due to gravity and the upthrust of the liquid act upon it when it is placed in air or water, as illustrated in the above figure. The upthrust lessens or neutralizes the weight because these two forces are directed in opposite directions. For instance, the force of gravity (W) equals the weight of the bottle (U) plus the upward force of the air on the plastic bottle. An upward thrust can overcome gravity's downward pull, which causes the weight of the bot and the bottle to sink or fall. Conversely, the upward thrust exceeds the bottle's weight when it is pushed down hard into the water. The submerged bottle emerges from the water when the upthrust overcomes gravity. The bottle floats in the water when the upthrust equals the bottle's weight. Thus, the upward force acting on an object when it is submerged entirely or partially in a gas or liquid (fluid) is referred to as upthrust. The Newton (N) is its SI unit.
A bucket will float in a well for a while, but as soon as it fills with water, it will become heavier. In that instance, the water's upthrust is insufficient to offset the bucket's downward force of gravity, causing the bucket to sink into the water. The upthrust applied to the bucket while it is submerged helps to reduce its weight. In that instance, the bucket's weight is lower than its actual weight. As a result, pulling up the bucket while submerged in water requires less force than its actual weight. The air upthrust is very small when the bucket is pulled out into the air compared to the water's upthrust. The force needed to pull the bucket rises in that scenario. As a result, once the bucket is inside the well, it is simple to pull a full one.
The air-induced upthrust is not insignificant in any scenario. Plastic buckets, bottles, and other objects don't take up much airspace and have very little thrust on them. However, the aircraft undergoes a significant upthrust.
Cause of Upthrust
The arrows in the figure illustrate the force that water exerts on the surface of a cubic object submerged in water as a result of its pressure. With the exception of the upper and lower surfaces, all surfaces are subject to equal and oppositely directed forces. As a result, the forces acting on the left and right surfaces cancel each other out, and the force acting on the front surface cancels out the force acting on the rear surface.
The object submerged in the liquid experiences normal pressure from all sides. As the object gets deeper, the pressure gets stronger. The pressure and force on the cubical object's lower surface are greater than those on its upper surface because the lower surface is located at a deeper depth. As a result, the object lessens the force on the lower surface and directs the remaining force upward. As a result, the upthrust is pointing upward.
Calculation of the Upthrust Acting on a Stone Immersed in Water
An object's weight is found to decrease when it is submerged in a liquid because of the upthrust applied to it. Real weight (W1) is the weight of an object measured in air; apparent weight (W2) is the weight of an object measured in a liquid. As a result, the upthrust that results from submerging an object in liquid can be expressed using the following formula:
Upthrust (U) = Actual weight (W1) - Unreal weight (W2)
Factors Affecting Upthrust
- Density of Liquid
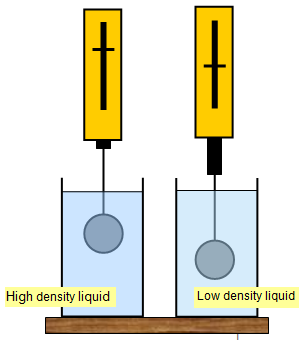
Water has a density of 1 gram per cent and edible oil has a density of 0.90 grams per cent. The stone in the activity above weighs less in water than it does in edible oil. Water exerts a greater upthrust than edible oil because its density is greater than that of the latter. As a result, the upthrust applied to a body is directly related to the liquid's density. As a result, the liquid with a higher density will exert a greater thrust on an object when it is submerged first in a lower-density liquid and then in a higher-density liquid.
Upthrust α Density of liquid
The iron ball sinks in water but floats on the surface of mercury because the upthrust is directly proportional to the density of the liquid. Mercury has a high density. Similarly, an egg dropped into a glass that was more than half filled with tap water sinks, as Figure illustrates. However, the egg begins to float once the salt has dissolved in the water. Compared to tap water, salted water has a higher density. Because of this, tap water lacks the upthrust that salty water does. Consequently, the egg floats in salt water but sinks in tap water. This explains why swimming in seawater is simple. A ship sinks less in seawater than in river water in a similar manner.
Because of this, tap water lacks the upthrust that salty water does. Consequently, the egg floats in salt water but sinks in tap water. This explains why swimming in seawater is simple. A ship sinks less in seawater than in river water in a similar manner.
- Volume of Liquid Displaced
 The figure illustrates the weight of a solid cylindrical object at various water immersion times. The figure illustrates how the reading on the spring balance decreases as the object's submerged portion's volume rises. The solid displaces more volume the longer it is submerged in water. The spring balance displays a constant reading once the object is fully submerged in water.
The figure illustrates the weight of a solid cylindrical object at various water immersion times. The figure illustrates how the reading on the spring balance decreases as the object's submerged portion's volume rises. The solid displaces more volume the longer it is submerged in water. The spring balance displays a constant reading once the object is fully submerged in water.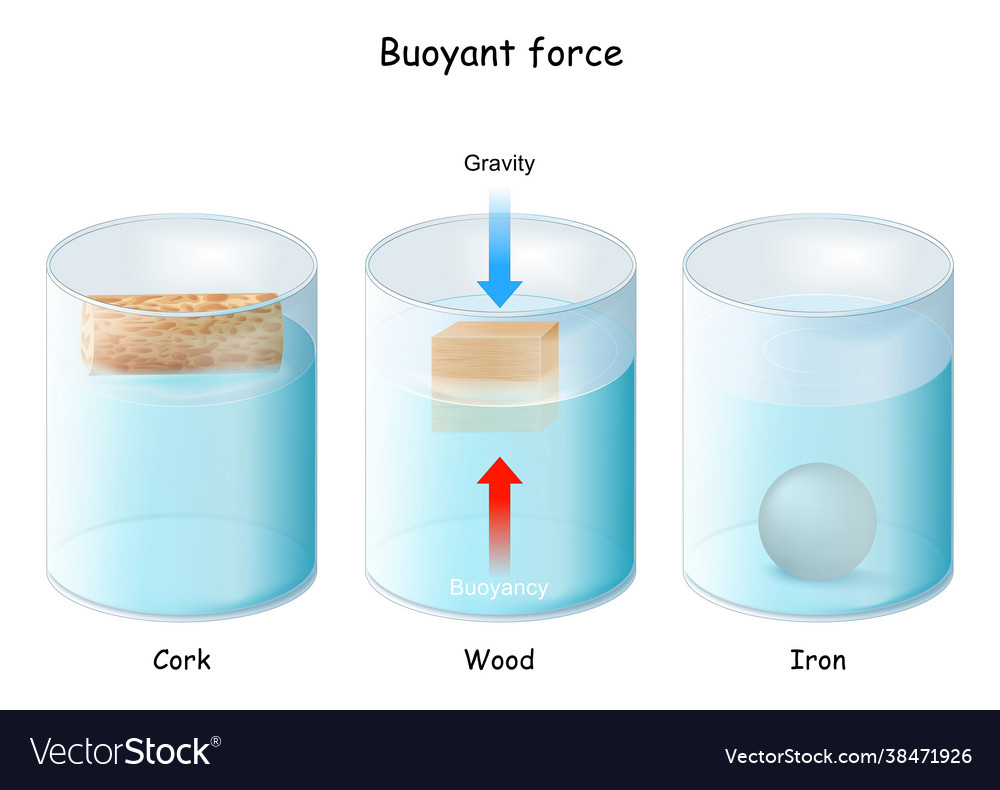 The 'upthrust' on a solid object submerged in a liquid increases with the volume of the object within the liquid; the upthrust reaches its maximum when the object is fully submerged. The upthrust doesn't change once the object is submerged in the liquid, despite the object's increasing depth. For instance, when two cubic solids with equal volumes but different weights are fully submerged in a liquid, the upthrust that acts on them is the same as what is depicted in Figure. As a result, the upthrust exerted on an object when it is submerged entirely or partially in a liquid is directly proportional to the volume of the displaced liquid. This implies that the upthrust acting on an object submerged in liquid increases along with the object's volume.
The 'upthrust' on a solid object submerged in a liquid increases with the volume of the object within the liquid; the upthrust reaches its maximum when the object is fully submerged. The upthrust doesn't change once the object is submerged in the liquid, despite the object's increasing depth. For instance, when two cubic solids with equal volumes but different weights are fully submerged in a liquid, the upthrust that acts on them is the same as what is depicted in Figure. As a result, the upthrust exerted on an object when it is submerged entirely or partially in a liquid is directly proportional to the volume of the displaced liquid. This implies that the upthrust acting on an object submerged in liquid increases along with the object's volume.
Upthrust α Volume of liquid displaced
When trying to submerge a big water-tight plastic bottle and a small water-tight plastic bottle, the big bottle displaces more water than the smaller one. Consequently, a big plastic bottle feels more upthrust. As a result, larger plastic bottles require more force to submerge in water than smaller bottles. Both large and small balloons filled with helium gas have the same effect. The upthrust acting on the large balloon is greater because it displaces more air than a small balloon. Archimedes' principle provides the relationship between the upthrust on an object and the weight of the displaced fluid when the object is submerged in a fluid.
Archimedes' principle provides the relationship between the upthrust on an object and the weight of the displaced fluid when the object is submerged in a fluid.
Things to remember
- An upward thrust can overcome gravity's downward pull, causing the object and the bottle to sink or fall.
- The upward force acting on an object when it is submerged entirely or partially in a gas or liquid (fluid) is referred to as upthrust, with the Newton (N) being its SI unit.
- The upthrust on an object when submerged in a liquid is determined by the actual weight (W1) and the apparent weight (W2).
- Higher-density liquids exert greater thrust on an object when submerged in lower-density liquids and higher-density liquids.
- Archimedes' principle provides the relationship between the upthrust on an object and the weight of the displaced fluid when the object is submerged in a fluid.
© 2021 Saralmind. All Rights Reserved.




 Login with google
Login with google