Greenhouse Effect and Acid Rain
Subject: Science

Overview
The greenhouse effect is a process where solar energy is trapped within greenhouses to raise their internal temperature, causing climate change. Natural greenhouses, made of clear glass or plastic, support plant development and preserve vegetation, while artificial greenhouses, made of clear glass or plastic, trap sunlight. The Earth's atmosphere is made up of gases like carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, chlorofluorocarbons, and ozone, which redirect sunlight towards the planet's surface. The rising concentration of greenhouse gases due to pollution, industrialization, and human activity exacerbates the greenhouse effect, leading to climate change and negative consequences. To reduce the greenhouse effect, strategies include controlling greenhouse gas production, promoting renewable energy sources, reducing carbon dioxide production, organizing plantation campaigns, and reducing acid rain. Strategies to stop acid rain include reducing sulfur and nitrogen oxides, substituting renewable energy sources for fossil fuels, increasing public awareness, filtering and purifying water, limiting pollution, promoting renewable energy sources, and reducing energy consumption.
Greenhouse Effect
Greenhouses are translucent glass or plastic buildings that retain solar heat to support healthy plant development and preserve vegetation. The greenhouse effect is the process of trapping solar energy within greenhouses to raise their internal temperature. You can utilize natural or artificial greenhouses. The homes constructed of clear plastic and glass are artificial greenhouses, whereas the soil itself is a natural greenhouse.
The natural greenhouse effect is the mechanism by which the surface of the planet warms. A portion of the solar radiation is reflected back and a portion is absorbed by the earth when it reaches the surface. Layers of greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), ozone (O3), etc., make up the earth's atmosphere. These gases redirect a portion of the sun's energy towards the earth's surface.
The atmosphere's concentration of greenhouse gases is rising as a result of pollution, industrialization, and human activity. As a result, more solar energy is reflected back to the surface of the planet, obstructing its escape into space. As a result, human activity exacerbates the greenhouse effect. A layer of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere is essential. Earth's temperature would be extremely low in the absence of greenhouse gases, which would mean that there would be no life on Earth. Because of the rise of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, the earth's temperature has been rising unnaturally. We are now dealing with climate change, which has a variety of detrimental effects.
Consequences of Greenhouse Effect
- Temperature rising
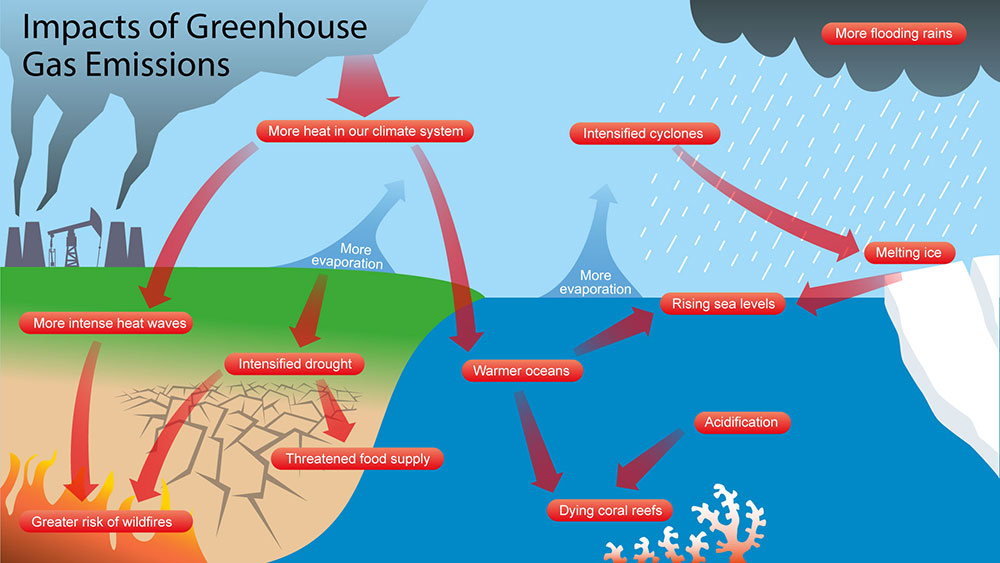
- Water cycle changing
- Harmful effects on people's health
- Harmful effects on people's health
- Snowfall in the Himalayas and on glaciers is decreasing due to melting.
- Coastal regions sinking and flooding due to sea level rise
- Decline of biodiversity
- Deforestation
- Ecosystem imbalance
Artificial Greenhouse
Because artificial greenhouses are constructed of clear glass or plastic, sunlight may penetrate them. Another name for them is "hot houses". A greenhouse is a glass and plastic building used to house plants. When short waves of solar radiation enter a greenhouse and absorb part of the energy, they transform into long waves. From there, these long-wavelength waves are unable to escape. These radiations with long wavelengths convert to thermal energy. As a result, the greenhouse's interior temperature rises as heat is retained there. The term "artificial greenhouse effect" describes this.
Importance and Utility of Artificial Greenhouse
Plants of any season may be cultivated in a greenhouse because of its comfortable temperature. We can grow out-of-season veggies within it and make money that way. It is also possible to preserve the lives of plants that are in danger of going extinct because of the excessive cold. In a similar vein, uncommon plants that grow in cold climates can also be preserved. The following is a list of the benefits and uses of greenhouses:
- It may be used all year round to cultivate plants of any season.
- It benefits food crops in extremely cold climates.
- You may grow a variety of plants, fruits, green leafy vegetables, flowers, and other things in greenhouses.
- The greenhouses' plants have the power to reduce pollutants in the surrounding air.
- It is possible to cultivate summer plants throughout the winter.
- Summer-grown plants can also be cultivated in chilly climates.
What makes the planet a greenhouse by nature?
The atmosphere of the planet is made up of gases such as carbon dioxide, ozone, water vapor, etc. These gases enable solar radiation to reach the surface of the planet but prevent it from leaving after reflection. The rays are thereby imprisoned inside the earth. The earth's temperature rises as a result of greenhouse gas emissions. It serves the same purpose as glass in a man-made greenhouse. The earth is a natural greenhouse as a result.
Strategies to Reduce the Earth's Greenhouse Effect
Controlling the production and use of greenhouse gases is necessary to lessen the greenhouse impact. We may use the following strategies to achieve this:
- Chlorofluorocarbons must be completely outlawed in both manufacturing and usage.
- While using renewable energy sources should expand, using coal and petroleum products should decrease.
- It is important to encourage the use of alternative energy sources, such as hydroelectricity, wind, solar, and so on.
- Organizing the plantation campaigns.
- There has to be a decrease in carbon dioxide production.
Acid Rain
In 1960 AD, acid rain was first documented. 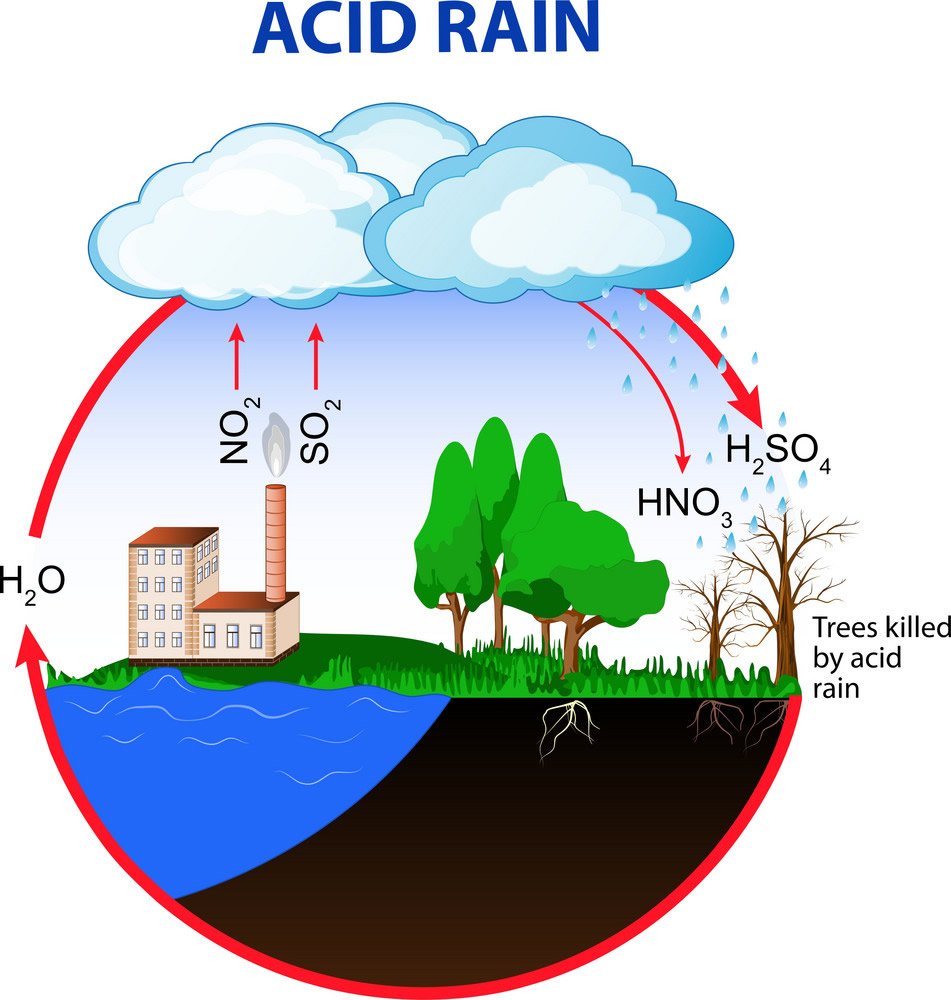 Acids such as sulfuric acid, carbonic acid, nitric acid, hydrochloric acid, and others are formed when gases from different businesses and automobiles combine with water vapor in the atmosphere. These gases include nitrous oxide, sulfur dioxide, carbon dioxide, and chlorine. Acid rain is the term used to describe the combination of these acids with precipitation. Rainwater is often acidic. It is at pH 6. Acid rain has a pH between 3 and 5.
Acids such as sulfuric acid, carbonic acid, nitric acid, hydrochloric acid, and others are formed when gases from different businesses and automobiles combine with water vapor in the atmosphere. These gases include nitrous oxide, sulfur dioxide, carbon dioxide, and chlorine. Acid rain is the term used to describe the combination of these acids with precipitation. Rainwater is often acidic. It is at pH 6. Acid rain has a pH between 3 and 5.
2SO2 + O2 → 2SO3
SO3 + H2O → H2SO4
CO2 + H2O → H2CO3
Effects of Acid Rain on the Earth
- Marble monuments, such as temples, buildings, statues, etc., are fading due to acid rain.
CaCO3(s) + H2SO4(aq) ⇄ CaSO4(s) + CO2(g) + H2O(I) - It makes the soil more acidic, which lowers productivity.
- When acid rain mixes with water sources, it affects aquatic creatures.
- It increases the chance of skin diseases in humans.
- It has a detrimental impact on people's health.
Strategies to Stop Acid Rain
- Decreased synthesis of sulfur and nitrogen oxides.
- Substitution of renewable energy sources for fossil fuels.
- Increasing public knowledge of acid rain's sources and consequences.
- Before releasing the factory-used water back into the rivers, filter and purify it.
- Limit the amount of pollution and gases an industry emits.
- Promote the use of renewable energy sources in place of fossil fuels.
- Cut down on the amount of energy that businesses and manufacturers use.
Things to remember
- The greenhouse effect is a process where solar energy is trapped within buildings to raise their internal temperature, leading to climate change and various negative consequences.
- The concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere is increasing due to pollution, industrialization, and human activity, which redirects sunlight towards the Earth's surface.
- Artificial greenhouses, made of clear glass or plastic, absorb long-wavelength solar radiation and convert it into thermal energy, raising the interior temperature.
- To reduce the greenhouse effect, strategies include controlling greenhouse gas production and usage, outlawing chlorofluorocarbons, expanding renewable energy sources, reducing coal and petroleum use, encouraging alternative energy sources, organizing plantation campaigns, and reducing carbon dioxide production.
- Acid rain, formed when gases from businesses and automobiles combine with water vapor, has negative effects on the Earth, including fading marble monuments, soil acidification, aquatic creatures, skin diseases, and health.
- To stop acid rain, strategies include reducing sulfur and nitrogen oxide synthesis, substituting renewable energy sources for fossil fuels, increasing public awareness of acid rain's sources and consequences, filtering and purifying factory-used water before release, limiting pollution and emissions, promoting renewable energy sources, and reducing energy consumption by businesses and manufacturers.
© 2021 Saralmind. All Rights Reserved.

 Login with google
Login with google