Hydrocarbons
Subject: Science

Overview
Chemicals can be classified into organic and inorganic groups, or carbonic and non-carbonic groups. Organic compounds, derived from plants and animals, are composed of carbon and hydrogen. Hydrocarbons are carbonic chemicals made of carbon and hydrogen and are used in various applications, such as cooking food and heating utensils. Organic chemistry studies these substances, with petroleum being the primary source. Saturated hydrocarbons are stable and less reactive, while unsaturated hydrocarbons contain two or three covalent bonds. Homologous series are hydrocarbons expressed using the same general formula, while functional groups determine the structure and chemical reactivity of organic compounds. Hydrogenation is the process of making vanaspati ghee from vegetable oil, which converts unsaturated fatty acids into saturated fatty acids.
Different kinds of chemicals are all around us. These substances can be divided into organic and inorganic groups or carbonic and non-carbonic groups. Non-carbonic chemicals, also known as inorganic compounds, are derived from minerals, whereas carbonic compounds, also known as organic compounds, are derived from plant and animal sources. With the exception of its oxides, carbonates, bicarbonates, and carbides, all carbon compounds are classified as organic. Hydrocarbons are carbonic chemicals that are solely made of carbon and hydrogen.
Hydrocarbon
The elements of all flammable materials are carbon and hydrogen. Carbon and hydrogen combine to form hydrocarbons. In communities without hydroelectric power, kerosene lights are lit. In a similar vein, food is cooked using firewood. In laboratories, spirit lights are utilized as a heat source. When creating utensils, metal is heated and melted using charcoal. These flammable materials are all composed of carbon and hydrogen. These materials come from both plants and animals.
Combustible materials derived from plants and animals are referred to as organic compounds. Protein, hormones, carbohydrates, fats, enzymes, protoplasm, and other materials that are found in the human body are all examples of organic molecules.
Organic Compounds
Organic compounds are generally defined as those in which one carbon atom is covalently bound to another carbon atom or a hydrogen atom. In addition to hydrogen, other elements such as oxygen, nitrogen, halogens, sulfur, and phosphorus may also form covalent bonds with carbon. Despite having carbon atoms, CO2, CO, HCO3-, and CO3-- are not organic molecules. In general, components like carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, halogen, sulfur, and phosphorus make up organic molecules.
Additionally, certain chemical molecules could have metal bound to them. Methane, ethane, ethene, acetylene, methanol, chloroform, urea, insulin, protein, oil, etc. are some examples of organic molecules. Organic chemistry, often known as carbonic chemistry, is the area of science that studies these substances. The primary source of hydrocarbons is petroleum. The kinds of bonds that exist between the carbon atoms in hydrocarbons determine whether they are unsaturated or saturated.
Saturated Hydrocarbon
Saturated hydrocarbons are hydrocarbons with only one covalent connection forming between the carbon atoms. They are referred to as paraffin because they are extremely stable and less reactive. Another name for them is alkanes. These compounds have the general formula CnH2n +2, where 'n' is the number of carbon atoms. Here n = 1, 2, 3, 4,...
| Name | Molecular Formula | Condensed Formula | Structural Formula |
| Methane | CH4 | CH4 | |
| Ethane | C2H6 | H3CCH3 |  |
| Propane | C3H8 | H2C(CH2)CH3 | |
| Butane | C4H10 | H3C(CH2)2CH3 |  |
| Pentane | C5H12 | H3C(CH2)3CH3 |
Unsaturated Hydrocarbon
Unsaturated hydrocarbons are defined as those that contain two or three covalent bonds between their carbon atoms. They are referred to as olefins because they are highly reactive and less stable.Alkene and alkyne are other names for them.
Alkene
Alkenes are hydrocarbons in which the carbon atoms have formed two covalent bonds. As an example, consider butene, propene, and ethene. The formula for these compounds is typically CH, where 'n' represents the number of carbon atoms.
| Name | Molecular formula | condensed formula | Structural formula |
| Ethen | C2H4 | H2C = CH2 | |
| Propan | C3H6 | H3C- CH = CH2 | |
| Butane | C4H8 | H3C- CH2- CH = CH2 |
Alkyne
Alkyne hydrocarbons are defined as those that have three covalent bonds forming between their carbon atoms. For instance, butyne, propyne, and ethyne. These compounds generally have the formula CH, where 'n' is the number of carbon atoms.
| Name | Molecular formula | condensed formula | Structural formula |
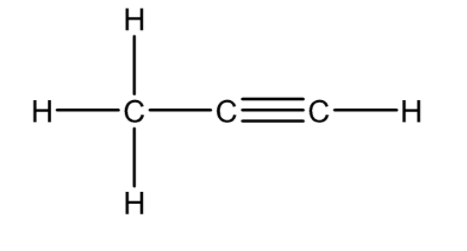
| Ethene | C2H2 | HCº CH | H-CºC-H |
| Propane | C3H4 | H3C-CºCH | |
| Butane | C4H6 | H3C-CH2-CºCH |
The process of making vanaspati ghee from vegetable oil is called hydrogenation. In hydrogenation, the unsaturated fatty acids change to saturated fatty acids.
H2C=CH2 (Alkene) + H2 → C2H6 (Alkane)
Differences Between Saturated and Unsaturated Hydrocarbons
| Saturated Hydrocompound | Unsaturated Hydrocarbon |
|
A saturated hydrocompound, also known as a saturated hydrocarbon, is a type of organic compound consisting entirely of carbon and hydrogen atoms linked by single bonds. |
Unsaturated hydrocarbons are those in which there are two or three covalent bonds forming between the carbon atoms. |
|
The general formula for saturated hydrocarbons is CnH2n+2, where "n" is the number of carbon atoms. |
The general formula for alkenes is CnH2n, and for alkynes, it is CnH2n-2. |
| Saturated hydrocarbons are typically more stable and less reactive compared to unsaturated hydrocarbons. | Unsaturated hydrocarbons are generally more reactive than saturated hydrocarbons due to the presence of the multiple bond. |
Homologous Series
A homologous series is a set of hydrocarbons that can all be expressed using the same general formula. Every person in this series is referred to as a homologue. The neighboring homologue of the series varies by CH2 group, and all members of the series may be described by a single formula. Likewise, there is a 14.2 molecular weight difference between neighboring members of the series or homologue.
| Name | Molecular Formula |
| Methanol | CH3OH |
| Ethanol | CH3CH2OH |
| Propanol | CH3CH2CH2OH |
Alkyl Radical
The group of atoms formed by removing one hydrogen atom from an alkane molecule is called an alkyl radical. It can be represented by a general formula CnH2n+1. For example: -CH3+, -C2H5+, etc.
Functional Group
An atom or a group of atoms which determines the structure and chemical reactivity of a certain group of organic compounds is called a functional group. The functional groups get attached to the alkyl groups to form different groups of organic compounds. Example of functional groups -O-, -CHO, -COOH
Things to remember
- Hydrocarbons are composed of carbon and hydrogen and are used in various applications such as lighting, cooking, and creating utensils.
- Organic compounds are defined as those where one carbon atom is covalently bound to another carbon atom or a hydrogen atom.
- Saturated hydrocarbons are extremely stable and less reactive.
- Unsaturated hydrocarbons contain two or three covalent bonds between their carbon atoms.
- A homologous series is a set of hydrocarbons expressed using the same general formula.
© 2021 Saralmind. All Rights Reserved.

 Login with google
Login with google