Temperature
Subject: Science

Overview
The specific heat capacities of land and saltwater have an impact on the air circulation in coastal environments. Land and sand have a lower specific heat capacity, leading to a sea breeze and a land breeze. Thermometers measure temperature using glass thermometers with mercury inside, digital thermometers with an electric circuit, and radiation thermometers. Calibration involves determining the scale's fixed points, which vary depending on the scale. The lower and higher fixed points of the Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Kelvin scales are 0°C and 100°C, respectively. Thermometers play a crucial role in regulating temperatures near coastal locations.
The air constantly circulates between the land and the sea in a coastal environment because of the difference in the specific heat capacities of the land and saltwater.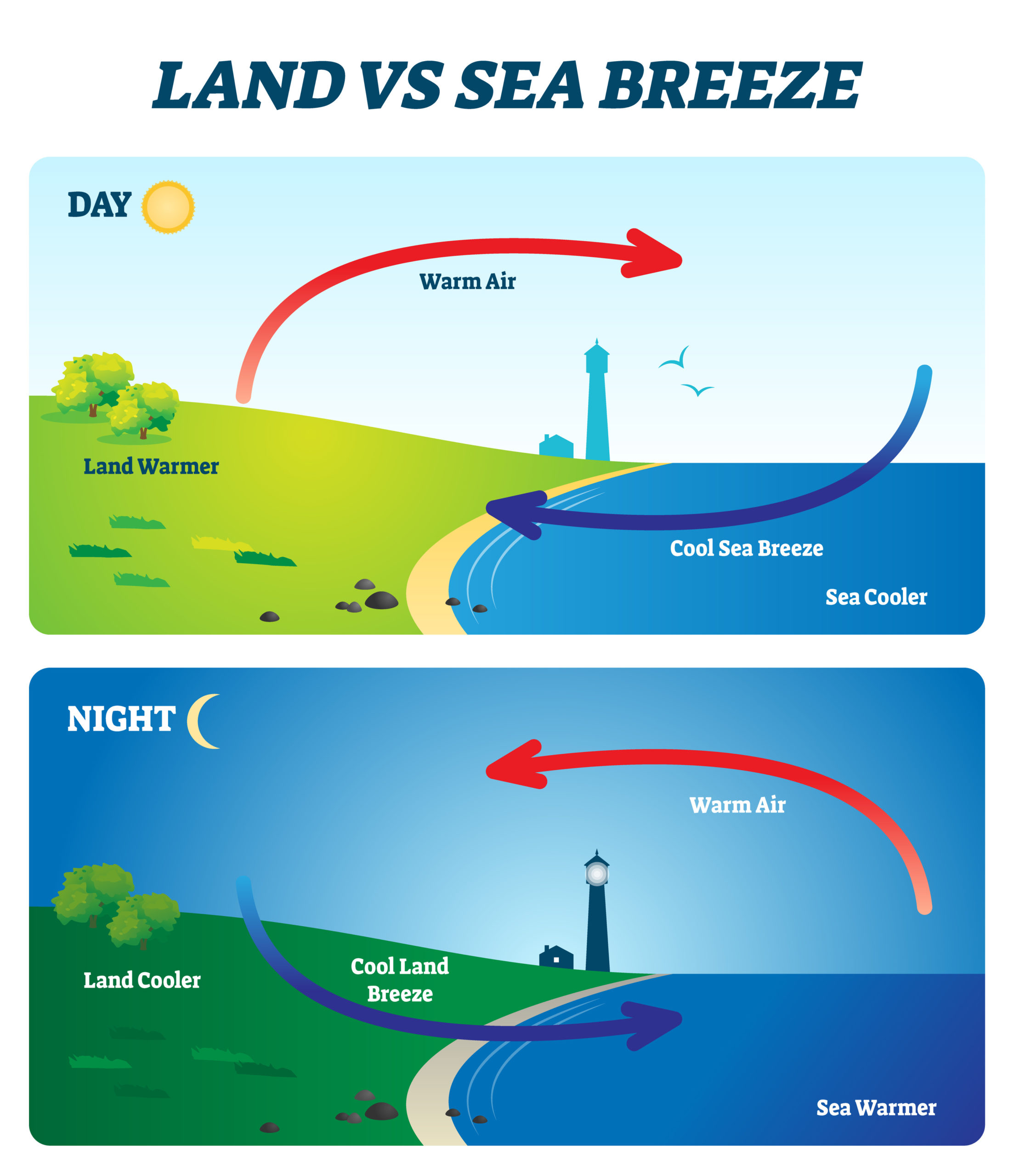 The land and the water receive equal heat from the sun in the afternoon. However, terrestrial temperature rises more quickly than sea level because land and sand have a specific heat capacity that is around five times lower than that of water. As a result, there is a low pressure area above the surface as the warm, light air above the earth rises. The upshot is that the sea's chilly air starts to move toward the land. We refer to this as a sea breeze.
The land and the water receive equal heat from the sun in the afternoon. However, terrestrial temperature rises more quickly than sea level because land and sand have a specific heat capacity that is around five times lower than that of water. As a result, there is a low pressure area above the surface as the warm, light air above the earth rises. The upshot is that the sea's chilly air starts to move toward the land. We refer to this as a sea breeze.
As a result of the radiation they emit at night, the temperature of the land and water drops. The temperature of land drops quickly when compared to the temperature of the ocean. The temperature of seawater stays higher at night than that of land due to the larger specific heat capacity of water. Consequently, cold air moves from the land to the sea and air pressure above sea level decreases while warm air over saltwater rises. We refer to this as the land breeze.
Because of the wind that blows from the sea to the land during the day and from the land to the sea at night, the temperature near coastal locations changes greatly between day and night.
Measurement of Temperature
Different types of thermometers and their working principles are listed in the following points:
- Glass thermometer with liquid inside
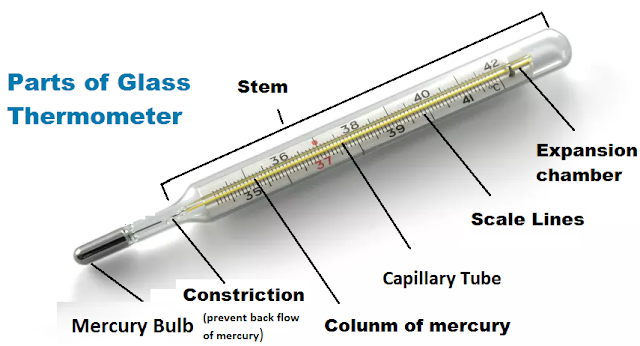 Within a heat-sensitive bulb, a thermometric liquid is housed in a glass thermometer. Mercury is a high-density thermometric liquid and an excellent heat conductor. A thermometer's bulb expands when it comes into contact with a hot item because heat is transmitted from the object to the mercury. Through the capillary tube that is connected to the bulb, the enlarged mercury travels forward. The point at which the mercury stops expanding serves as a gauge of the object's temperature. The scale on the outside wall of the glass thermometer is used to read the temperature of a liquid.
Within a heat-sensitive bulb, a thermometric liquid is housed in a glass thermometer. Mercury is a high-density thermometric liquid and an excellent heat conductor. A thermometer's bulb expands when it comes into contact with a hot item because heat is transmitted from the object to the mercury. Through the capillary tube that is connected to the bulb, the enlarged mercury travels forward. The point at which the mercury stops expanding serves as a gauge of the object's temperature. The scale on the outside wall of the glass thermometer is used to read the temperature of a liquid.
- Digital Thermometer
 This device measures an object's temperature by means of an electric circuit and a heat-sensitive thermistor. When using the thermometer, turn it on and contact the body with the thermistor's end. Heat from the body increases the thermistor's resistance, which modifies the electric current passing through the circuit. This tweak causes the detected temperature to now appear as a number on the display screen.
This device measures an object's temperature by means of an electric circuit and a heat-sensitive thermistor. When using the thermometer, turn it on and contact the body with the thermistor's end. Heat from the body increases the thermistor's resistance, which modifies the electric current passing through the circuit. This tweak causes the detected temperature to now appear as a number on the display screen.
- Thermometer for radiation
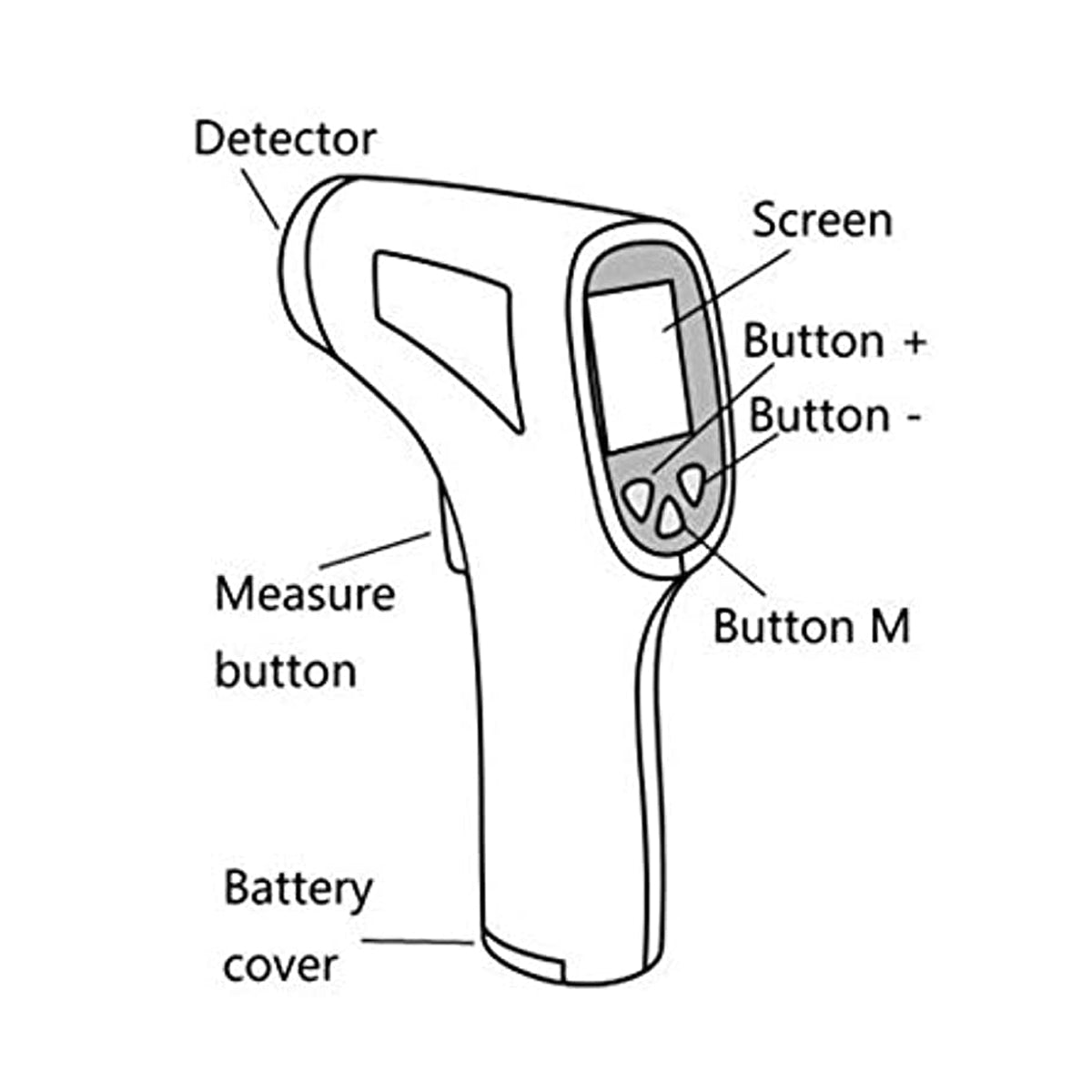 It is a non-contact thermometer for taking a body's temperature. The strength of the infrared radiation that the human body produces determines the mechanism of operation. The sensor must be facing the body in order to be used. The device's lens concentrates the infrared light that the thing on the sensor is emitting. Electrical signals are produced based on the heat transported by radiation, and the object's temperature is shown on the display screen. Temperatures may be measured quickly and easily using this kind of thermometer.
It is a non-contact thermometer for taking a body's temperature. The strength of the infrared radiation that the human body produces determines the mechanism of operation. The sensor must be facing the body in order to be used. The device's lens concentrates the infrared light that the thing on the sensor is emitting. Electrical signals are produced based on the heat transported by radiation, and the object's temperature is shown on the display screen. Temperatures may be measured quickly and easily using this kind of thermometer.
Calibration of Thermometer
Determining a thermometer's scale is the process of calibration. The distance between the two fixed points (upper fixed point and lower fixed point) is first calculated and subsequently split into the required number of equal pieces. When calibrating a thermometer, the temperature at which ice melts (0°C) is considered the lower fixed point, and the temperature at which steam boils at atmospheric pressure (100°C) is considered the higher fixed point. Next, divide the distance between these two places into 100 equal parts, with each part denoting a temperature of 10 °C.

The fixed points vary depending on the thermometer's scale. The lower and higher fixed points of the Celsius scale are, respectively, 0°C and 100°C.The bottom and upper bounds of the Fahrenheit scale are 32°F and 312°F, respectively. In the same way, 273K and 373K are considered to be the lower and upper limits of the Kelvin scale, respectively.
Things to remember
- At night, the temperature drops due to radiation from the sea, causing cold air to move towards the land and air pressure to decrease.
- Glass thermometers use mercury as a heat conductor.
- Digital thermometers use an electric circuit and a heat-sensitive thermistor.
- Radiation thermometers use infrared radiation to measure body temperatures.
- Calibration involves determining the scale by dividing the distance between fixed points, such as the temperature at which ice melts (0°C) and the temperature at which steam boils at atmospheric pressure (100°C).
© 2021 Saralmind. All Rights Reserved.

 Login with google
Login with google