Metallurgy
Subject: Science

Overview
Mining is the process of extracting minerals and other materials from the Earth's surface, including metal ores like coal, oil, and gold. Metallurgy studies the composition, synthesis, and purification of metals. To extract pure metal from ores, five basic stages should be followed: grinding, concentration, oxidation, smelting, refining, distillation, and electro-refining. Grinding breaks down ores into tiny particles, while concentration purges impurities from ores. Oxidation converts ores to metal oxides, while smelting removes impurities. Refining removes impurities from recovered metals, and distillation purifies low boiling points and vaporizes. Electro-refining, a method of refining metals from reduction, yields 99% pure metals.
Mining
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-164852650-74b47d6b10d0436c9e8b2ed910134d9d.jpg) In order to extract metals, the earth's surface must first be dug up in order to remove the metals' ores. Mining is the process of removing minerals and other useful materials from the earth's geological surface. Mining is a method of extracting metal ores such as coal, oil, gold, and others from the earth's crust. Subsequently, various procedures are used to remove metals from their ores.
In order to extract metals, the earth's surface must first be dug up in order to remove the metals' ores. Mining is the process of removing minerals and other useful materials from the earth's geological surface. Mining is a method of extracting metal ores such as coal, oil, gold, and others from the earth's crust. Subsequently, various procedures are used to remove metals from their ores.
The science that studies the composition, synthesis, and purification of metals is called metallurgy. It also covers the methodical process of removing metals from their corresponding ores. To extract pure metal from their ores, five basic stages should be followed.
General Steps of Metallurgy
Grinding
The process of extracting metal begins here. Grinding is the process of breaking down ores into tiny particles with the aid of machine rollers.
Concentration
Gangue is the term for impurities found in crushed or grounded ores, such as sand, pebbles, and mud. So, it is necessary to eliminate these pollutants first. The process of concentration is used to purge ores of contaminants. Therefore, concentration refers to the process of purging impurities from ores in order to raise the proportion of metals in them. Depending on the impurities' characteristics, a particular technique is applied to extract them from the ores. For instance, a hydraulic or gravity separation method is applied if the ore and impurity densities differ. Likewise, in the event that one of them is magnetic and the other is not, magnetic separation is employed. In cases where certain contaminants are hydrophilic and others are hydrophobic, the concentration of the ore.
Oxidation
Concentrated ores are converted to metal oxide because it is simpler to extract metals from their oxides. Metals oxidize through two distinct mechanisms.
- Roasting
It involves heating the ore to high temperatures in the presence of oxygen or air. On non-oxide ores, this procedure is carried out. Roasting is typically done to change sulfuride ores into their oxide counterparts. For instance, roasting transforms zinc sulphide (ZnS) into zinc oxide (ZnO). - Calcination
It involves heating the ores to their oxides at high temperatures without the presence of air or oxygen. The process of calcination yields the oxides of carbonate ores. A calcination procedure, for instance, is used to change calcium carbonate into calcium oxide.
Reduction
It's the procedure that takes oxygen out of metal oxide. Reducing agents such as carbon, carbon monoxide, hydrogen, etc. are used to treat metal oxides such as copper oxide, lead oxide, and iron oxide in order to extract their oxygen. However, only carbon can decrease zinc oxide. Heat causes the unstable oxides of silver and mercury to decrease. Reactive metal oxides, such as those of sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, aluminum, etc., are extremely stable and can only be decreased by the electrolysis process.
- Smelting
After oxidation, metal oxides react with hydrogen, carbon, or coke, or other reducing chemicals that are above the melting point of the metals. Metals are extracted from their oxides during this process while they are still molten, and any remaining impurities are removed as slag or gases. Smelting is the process of heating metals over their melting temperatures while combining them with a reducing chemical.
Refining
After the reduction process, some impurities might still be present in the metals that are recovered. Thus, refining is done to obtain metals in their pure state. A variety of techniques, including electrorefining and distillation, can be used to refine metals. In this way, after refining using several techniques, pure metals can be obtained.
- Distillation
The procedure of boiling away impurities from metals is used to purify metals that have low boiling points and vaporize, like mercury. This process is carried out when the metals or impurities evaporate when heated.
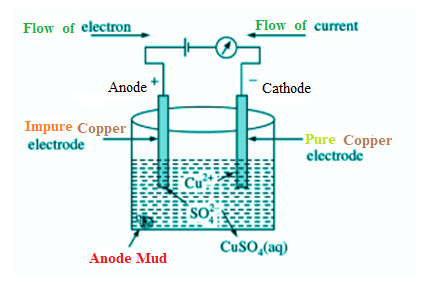
- Electro-refining
One method of refining metals that come from the reduction process is electro-refining. The electrolysis method is employed for electro-refining. This method can produce pure metals such as iron, silver, copper, gold, etc. This method yields metals that are roughly 99% pure. Using a voltameter (an electrolysis vessel), impure metal is linked to the anode (the positive terminal of the cell) and pure metal is connected to the cathode (the negative terminal of the cell) in this procedure. One of the salts of the metal that has to be purified is utilized as an electrolyte in this process. Try purifying impure copper, for instance, using the electro-refining process.

Things to remember
- Metallurgy is the science that studies the composition, synthesis, and purification of metals.
- To extract pure metal from ores, five basic stages should be followed: grinding, concentration, oxidation, smelting, refining, distillation, and electro-refining.
- Grinding breaks down ores into tiny particles using machine rollers.
- Concentration purges impurities from ores to increase their proportion of metals.
- Techniques like hydraulic or gravity separation, magnetic separation, and hydrophilic/hydrophobic separation are used depending on the impurity's characteristics.
- Oxidation converts concentrated ores to metal oxides, which are then oxidized through roasting, calcination, reduction, smelting, refining, distillation, and electro-refining.
© 2021 Saralmind. All Rights Reserved.


 Login with google
Login with google