INTRODUCTION TO MICROBIAL WORLD
Subject: Basic Science Applied to Nursing

Overview
INTRODUCTION OF MICROBIOLOGY
The scientific field of microbiology is concerned with the investigation of microorganisms. The word "microbiology" is derived from the Greek words "mikros" (small), "bios" (life), and "logos" (study), and it refers to the study of living things that are invisible to the naked eye.
Historical Development of Microbiology
The observation of microorganisms had to wait until microscopes were developed because they are not visible to the unaided eye. The following scientists played major roles in the development of microbiology; their contributions are highlighted:
- Contribution of Antony Leewenhoek: Leewenhoek deserves credit for observing and describing microorganisms before Van. He created glass lenses with sufficient strength for viewing microorganisms. He characterized the rod, sphere, and spiral as three morphological forms of animalcules.
- Roberthook made a contribution by creating the compound microscope and validating Leewenhoek's finding.
- Louis Pasteur made contributions as a qualified chemist from France. He became interested in microbiology after studying wine fermentation. He is referred to as the Father or Founder of Microbiology.
His contributions in the field of Microbiology are:
i.. Development of methods and techniques of bacteriology
ii. Introduction of sterilization techniques and development of steam sterilizer, autoclave and hot air oven. Tyndall (student of Pasteur) introduced the method of sterilization by repeated heating (Tyndallization).
iii. Studies on anthrax, chicken cholera and hydrophobia. He suggested that the causative agent of rabies was too small to be seen by microscope.
iv. Introduction of attenuated live vaccine for prophylactic use. - Contribution of Joseph Lister: He was a professor of surgery. He applied Pasteur's work and introduced antiseptic technique in surgery for killing bacteria in wounds and air with carbolic acid. He is known as Father of antiseptic surgery.
- Contribution of Robert Koch: He was a German general practitioner. He is also known as the Father of Bacteriology. His contributions are as follows:
i. Perfected bacteriological techniques and introduced methods for isolation of pure strains of bacteria.
ii. Introduced methods of obtaining bacteria in pure cultures using solid media.
iii. Introduced staining techniques iv. Discovered the anthrax bacillus, tubercle bacillus and the cholera vibrios.
iv. Koch's postulates given by Robert Koch has following points:
a. The organism should be constantly associated with the lesions of the disease.
b. It should be possible to isolate the organism in pure culture from the lesions of the disease.
c. The isolated organism (in pure culture) when inoculated in suitable laboratory animals should produce disease.
d. It should be possible to re isolate the organism in pure culture from the lesions produced in the experimental animals.
e. The specific antibodies to the organism should be demonstrable in the serum of patients. - Contribution of Paul Ehrlich: He was German Scientist and is also known as Father of Chemotherapy. His contributions are:
i. Applied stains to cells and tissues for study of their functions
ii. Reported the acid-fast nature of tubercle bacillus.
iii. Proposed side chain theory of antibody production.
iv. Introduced the methods of standardizing toxin and antitoxin. - Contribution of Edward Jenner: Introduced the first successful immunization in small pox by live virus of cow pox.
- Contribution of Alexander Fleming: The discovery of penicillin by Fleming ushered in antibiotic era. accidentally discovered that substance produced by inhibited number He a mould. of disease producing organism and named it as 'Penicillin".
Branches of Microbiology
Microbiology has many branches, which can be briefly summarized below:
- Medical Microbiology:
It is the area of microbiology that focuses on the research of human-infecting microbes and the illnesses they cause in their human hosts. It also addresses how the body reacts to microorganisms. Medical microbiology can be discussed in terms of virology, bacteriology, mycology, parasitology, and immunology.
a. Virology: Virology is the name of the branch of microbiology that deals with the study of viruses. Since viruses lack a metabolic system outside of a living cell, they are not regarded as true living organisms.
b. Bacteriology: Bacteriology is the name of the area of microbiology that focuses on the study of bacteria. The prokaryotic and unicellular organisms are known as bacteria.
c. Mycobacteriology: Mycobacteriology is the area of microbiology that focuses on understanding bacteria of the genus Mycobacterium.
d. Parasitology: Parasitology is the name of the branch of microbiology that deals with the study of parasites. A variety of parasites, including protozoa, platyhelminthes, nematodes, etc., are included in this subfield of microbiology.
e. Mycology: The area of microbiology dedicated to the research of fungi. Because fungus can pose a serious threat to public health, mycology is a major branch of microbiology.
f. Immunology: Biology's field of immunology focuses on the body's defense mechanisms, immune response, and immunity. When the immune system is weak, diseases like autoimmunity, allergies, etc. result. - Food Microbiology:
It is a subfield of microbiology that focuses on the investigation of all facets of food microbiology. It focuses on the study of both the microorganisms that are necessary for food production and those that contaminate and spoil food. - Industrial Microbiology:
The use of microorganisms in industrial preparations is discussed. for instance, making cheese, wine, etc. Industrial. - Agricultural microbiology:
It is the research of microbes related to plants. Microbes that contribute to soil fertility and the growth of plant products are also discussed. - Pharmaceutical Microbiology:
It focuses on the investigation of microbes that could contaminate or even ruin pharmaceutical preparations. - Molecular Microbiology:
The area of microbiology that focuses on understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying microorganism replication, transcription, and translation
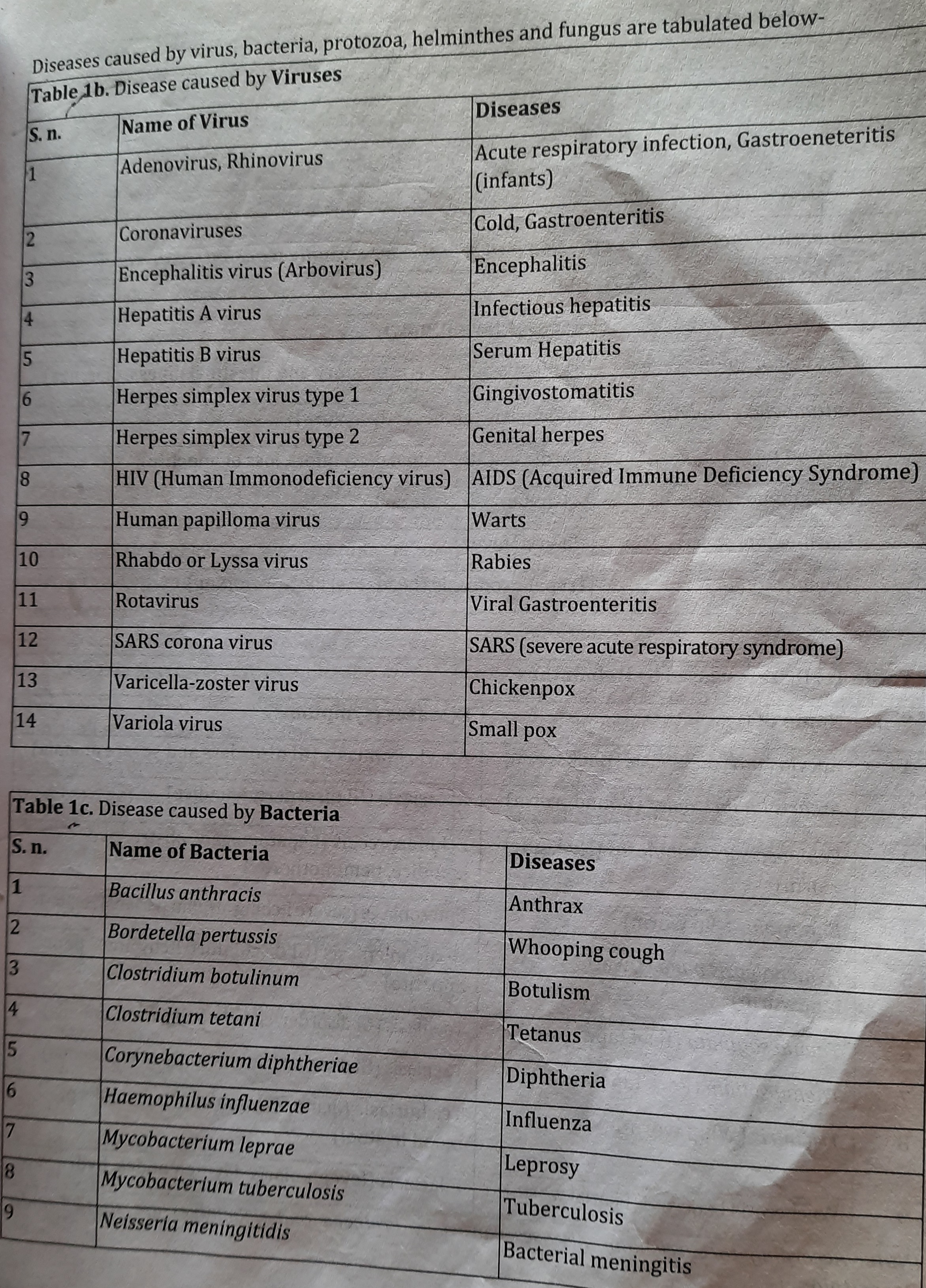
Classification of Microbial Diseases:
On the basis of microbial agents, microbial diseases are classified as:
a. Viral diseases
b. Bacterial diseases
c. Protozoan diseases
d. Helminthic diseases
e. Fungal diseases


MICROSCOPY
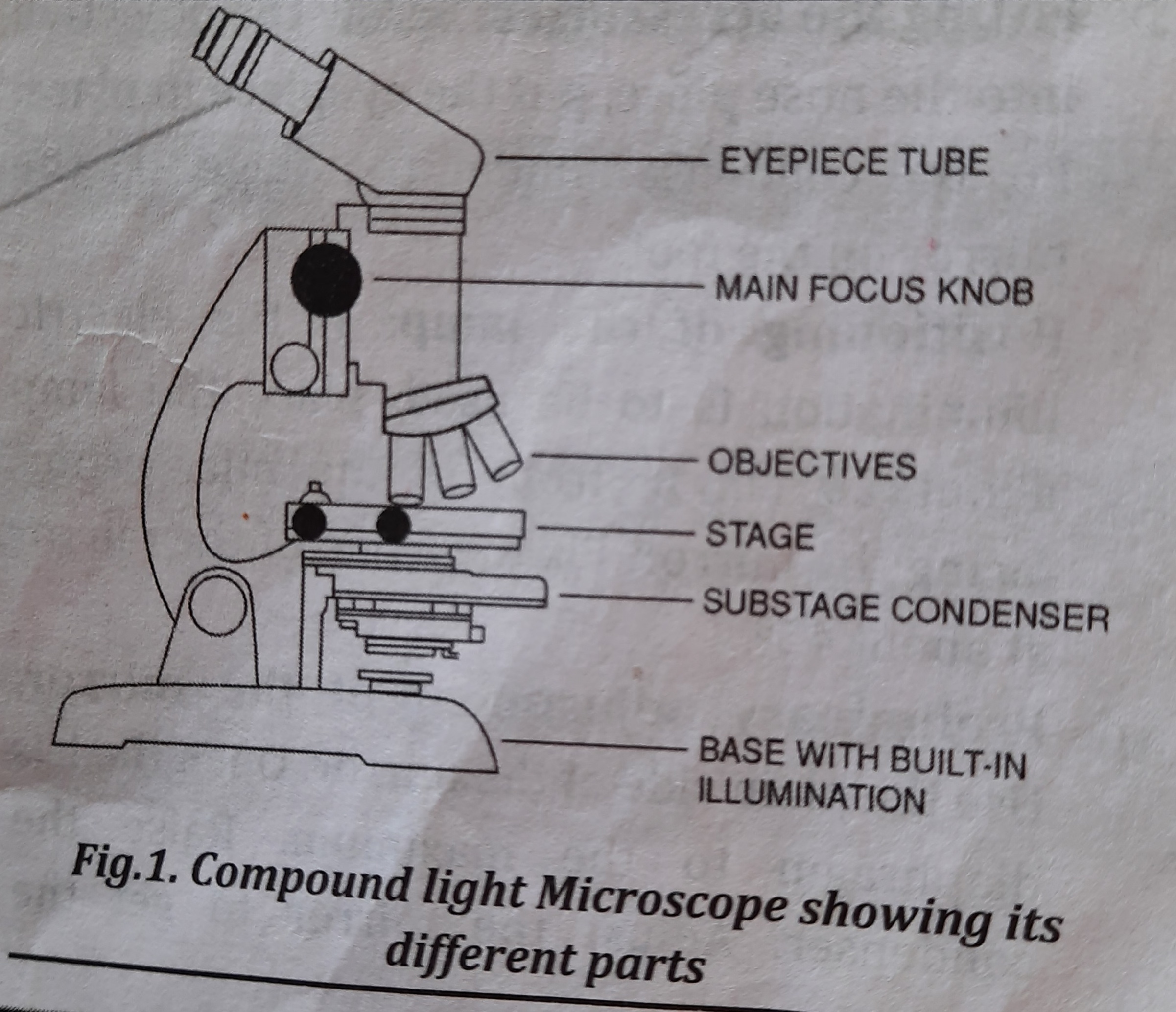
Microscope
A microscope is a crucial piece of equipment for a microbiology lab. It enlarges and lights the tiny items to make them visible, including bacteria and other microbes. Using a series of lenses and a powerful light source, a microscope magnifies and illuminates objects. The initial step in the identification and morphological study of organisms is a microscopical investigation. While bacteria must be identified using oil immersion microscopy, fungi and protozoa can be studied under low or medium power light microscopes.
Types of Microscopes:
The following types of microscopes are commonly used:
1. Optical or light microscope (The Compound microscope)
2. Phase contrast microscope
3. Dark ground (dark field) illumination (DGI)
4. Interference microscope 5. Fluorescent microscope
6. Electron microscope
Things to remember
© 2021 Saralmind. All Rights Reserved.

 Login with google
Login with google