Arrhythmia
Subject: Medical and Surgical Nursing I (Theory)

Overview
Disabilities is an umbrella term, covering impairments, activity limitations, and participation restrictions. An impairment is a problem in body function or structure; an activity limitation is a difficulty encountered by an individual in executing a task or action; while a participation restriction is a problem experienced by an individual in involvement in life situations. Disability is the consequence of an impairment that may be physical, cognitive, intellectual, mental, support sensory, developmental, or some combination of these that results in restrictions on an individual's ability to participate in what is considered "normal" in their everyday society. The cause of disability include genetic factors, birth asphyxia, prolong labor, difficult instrumental delivery, central nervous infection and so on.Management of children with special needs to be related to disability are provided support to the parents at the time of diagnosis of the child, Family-centered child care, Promote the normal development, encouragement.supportsand provide encouragement.
Cardiac Rythm Disorders
Arrhythmias
The Greek words rhymos, which means "rhythm," and a, which means "loss," are combined to form the English term "arrhythmia," which means "loss of rhythm." When the electrical impulses to the heart that regulate heartbeats are malfunctioning, this issue arises.
- An arrhythmia is an irregular heartbeat the heart may beat too fast (tachycardia), too slowly (bradycardia), too early (premature contraction) or too irregularly (fibrillation).
- Arrhythmia may be classified in various ways. According to origin arrhythmia may be ventricular or atrial.
- According to the heart rate; tachycardia (>100 beats per minute) or tachyarrhythmia and bradycardia (< 60 beats per minute).
Sinus Tachycardia
It is a condition where the heart rate is >100 beats per minute, originating in the SA node.
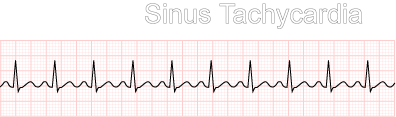
Causes of sinus tachycardia are fever, apprehension, physical activity, anemia, hyperthyroidism, drugs (theophylline, epinephrine) and caffeine etc. Clinical manifestations may include (1) Rate 100-160/m (2) Rhythm-regular (3) P wave- precedes each QRS complex with normal counter (4) P R interval- normal (0.08 sec) (5) QRS complex normal (0.06 sec). Management includes: Correct underlying cause. Eliminate of stimulants if present. Use sedatives and propranolol (inderal).
Sinus Bradycardia
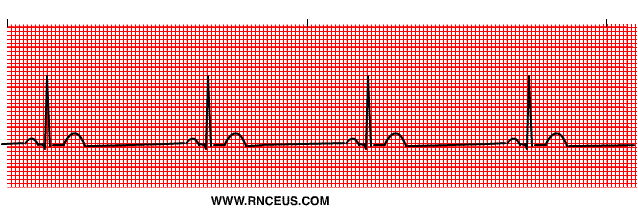
A slow heart rate initiated by SA node. It may be caused by excessive vagal stimulation or decreased sympathetic tone, MI and increased intracranial pressure etc. Assessment findings reveal normal ECG except heart rate > 60beats / m The treatment is usually not needed. If cardiac output is inadequate; (1) Atropine (2) soproterenol (Isuprel) can be used. If the drugs are not effective use pacemaker.
Atrial Fibrillation (AF)
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is an arrhythmia in which ectopic foci cause rapid, irregular contraction of the heart. AF is common in patients with rheumatic heart disease. emboli, cardiomyopathy, pericarditis, pulmonary emboli, ischemic heart disease and thyrotoxicosis. It causes minimal hemodynamic compromise and often the patient presents complaining of palpitations as the only symptom. Although hemodynamic compromise is minimal, atrial fibrillation is an important risk factor for the development of thromboembolic complications, such as strokes and transient ischemic attacks.
Assessment Findings on ECG
- Rate:
- Atrial: 350-600 beats/min
- Ventricular- varies between 100-160 b/m
- Rhythm-atrial and ventricular regularly irregular.
- P wave- no definite P wave; rapid undulations called fibrillatory(f) waves.
- PR interval- not measurable.
- QRS complex generally normal.
Management of AF
- Verapamil in conjunction with digitalis
- Direct current cardioversion
- Digitalis preparation
- Propranolol
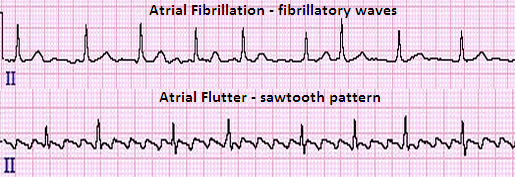
Atrial Flutter
The difference between atrial flutter and fibrillation is that flutter is well organized while fibrillation is not. It can come and go, as can atrial fibrillation, can be serious. A patient with atrial flutter will typically experience 250 to 350 beats per minute. It is relatively uncommon and is most often seen in patients presenting with acute ischemic heart disease or pulmonary embolism. Nevertheless, it can present as a chronic condition in patients who suffer from organic heart disease.
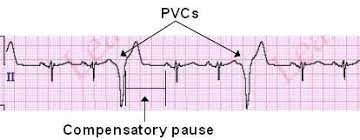
Premature Ventricular Contraction
Irritable impulses originate in the ventricles. Premature ventricular complex may arise in normal individuals as well as patients suffering from nearly every form of structural heart disease. Causes may be excessive catecholamines electrolyte imbalance (hypokalemia), digitalis therapy. myocardial ischemia, hypoxia, stimulants, CHF
Assessment findings on ECG
- Rate- varies according to number of VPCs.
- Rhythm-irregular because of VPCs.
- P wave-normal; however, often lost in QRS complex.
- PR interval- often not measurable.
- QRS complex- wide and distorted in shape, greater than 0.12 sec.
Management
- IV push of lidocaine (50-100mg) followed by IV dri of lidocaine at a rate of 0-4 mg / m.
- Procainamide (pronestyl), quinidine.
- Treat underlying cause.
Ventricular Tachycardia (VT)
A run of three or more consecutive VPCs, occurs from repetitive firing of an ectopic focus on the ventricle Ventricular tachycardia is defined as three or more ventricular complexes in succession at a rate than 100 bpm. Causes of VT includes acute MI, CA digitalis intoxication, hypokalemia etc. greater die
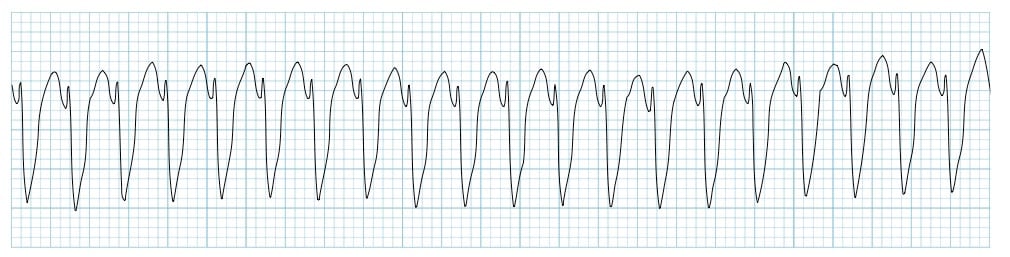
Assessment findings on ECG:
- Heart rate:
- Atrial: 60-100 b/m
- Ventricular: 100-250 beats/m
- Rhythm: atrial(regular), ventricular (occasionally irregular)
- P wave often lost in QRS complex.
- PR interval usually not measurable.
- QRS complex- greater than 0.12 sec wide.
Management of VT
- IV lidocaine (50-100mg), then IV drip of lidocaine 1-4 mg / m.
- Procainamide via IV infusion of 2-6 mg / m.
- Propranolol.
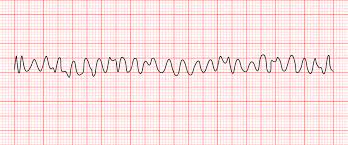
Ventricular Fibrillation (VF)
Irregular heart rhythm consisting of very rapid, uncoordinated fluttering contractions of the ventricles. The ventricles do not pump blood properly. Blood pressure drops dramatically, depriving vital organs, including the brain, of their essential blood supply. The majority of the patient loses consciousness quite quickly and require emergency medical assistance, including CPR. The patients who receive CPR until their heart can be shocked back into a normal rhythm with a defibrillator have much better survival rates.
If the patient does not receive CPR or defibrillation, he/she will die within minutes. Ventricular fibrillation is usually associated with some kind of heart disease. Ventricular brillation is often triggered by a heart attack.
Things to remember
- Disabilities is an umbrella term, covering impairments, activity limitations, and participation restrictions.
- An impairment is a problem in body function or structure; an activity limitation is a difficulty encountered by an individual in executing a task or action; while a participation restriction is a problem experienced by an individual in involvement in life situations.
- Disability is the consequence of an impairment that may be physical, cognitive, intellectual, mental, sensory developmental, or some combination of these that results in restrictions on an individual's ability to participate in what is considered "normal" in their everyday society.
- The cause of disability include genetic factors, birth asphyxia, prolong labor, difficult instrumental delivery, central nervous infection and so on.
- Management of children with special needs to be related to disability are
provide support to the parents at the time of diagnosis of the child, Family-centered child care, Promote the normal development, Family support and providing support and encouragement.
Questions and Answers
What is the management of children with a disability?
Management of children with special needs to be related to disability
- At the moment of the child's diagnosis, offer assistance to the parents.
- Childcare geared at families:
- Assist and provide knowledge on how to deal with daily routines including eating, dressing, and using the restroom.
- Give advice on how to manage the handicap condition, such as through exercise, etc.
- Give standard medical attention.
- Infection after harm.
- Dental wellness.
- Regular medical checkups
- Inform people about dangerous emergency conditions.
- Parents should be urged to identify their child's strengths.
- Encourage parents to maintain reasonable expectations in light of their child's abilities.
- Use a care strategy that honors the rights, aspirations, and potential of every kid.
- Children deserve your support and encouragement.
- Protect the kids from abuse, exclusion, and discrimination.
- Promote normal development:
- Promote the child's capacity for self-care in both everyday living activities.
- Instead of feeling sorry for them, give them opportunity to learn, support, and a good environment.
- Encourage kids to participate in social and physical activities.
- Describe the need for education, healthcare, and/or rehabilitation.
- Family support:
- Encouragement and assistance will help them accept the circumstance.
- Help the family encourage the child's proper development by providing guidance and support.
- Encourage and assist the family in coping with the condition with the child.
What are the causes of disability?
Causes
- Pre-natal factors:
- Genetic and chromosomal factors
- Congenital malformations
- Intra-natal factors:
- Birth asphyxia
- Prolonged labour
- Difficult instrumental delivery
- Post-natal factors:
- Hypoglycemia
- Hyperbilirubinemia
- Central nervous infection
Define disability?
The phrase "disabilities" is a general one that includes impairments, activity constraints, and participation limitations. An impairment is a problem with physical structure or function, an activity restriction is a challenge that a person faces when carrying out an action, and a participation restriction is a difficulty that a person encounters when taking part in activities of daily living. Disability is a complicated phenomenon that results from the interaction between a person's physical characteristics and those of the society in which they live.
© 2021 Saralmind. All Rights Reserved.


 Login with google
Login with google