Meconium Aspiration Syndrome
Subject: Child Health Nursing

Overview
A infant with meconium aspiration syndrome breaths a mixture of amniotic fluid and meconium into the lungs shortly after delivery. Meconium is a type of feces that develops in a fetus's intestines prior to birth and has a dark green color. Your baby may develop MAS if they are under stress. When the fetus has less oxygen accessible to it, stress frequently results. A pregnancy that lasts past the due date (more than 40 weeks), a challenging or protracted birth, and certain maternal health conditions, such as hypertension (high blood pressure) or diabetes, are common causes of fetal stress. Breathing problems, a lack of breathing, a greenish tint of the amniotic fluid, weight loss, and limpness at birth are signs and symptoms of MAS. The baby's throat and nose are suctioned as soon as the head is born, and if the infant continues to appear unwell and experience breathing difficulties, the laryngoscope is used to continue suctioning meconium from beneath the vocal cords. Complications of MAS include collapsed lungs, respiratory issues, and brain damage brought on by a lack of oxygen.
Meconium is a type of feces that develops in a fetus's intestines prior to birth and has a dark green color. A infant with meconium aspiration syndrome breaths a mixture of amniotic fluid and meconium into the lungs shortly after delivery.
Causes
- MAS may occur when your baby experiences stress. When the fetus has less oxygen available to it, stress frequently results. Fetal stress is frequently brought on by:
- An ongoing pregnancy after the due date (more than 40 weeks).
- Long or difficult labor.
- The mother's health problems, such as diabetes or hypertension (high blood pressure),
- A contamination.
- Diabetic mother
- High blood pressure in the pregnant mother.
Pathophysiology
Stress during labor may cause the fetal intestine to move more and the anal sphincter to loosen, which could lead to meconium passing into the adjacent amniotic fluid. If the child breathes while still in the uterus or while still being covered by this fluid after birth, the combination could reach the lungs and partially or fully clog the infant's airways.
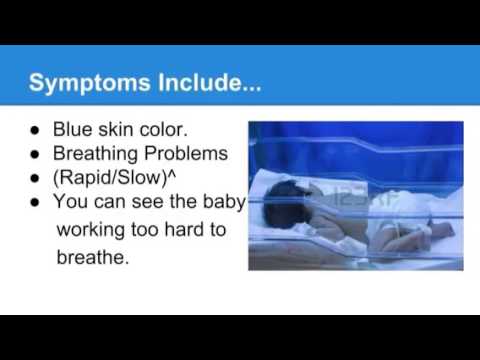
Signs and Symptoms
- Breathing problems
- Lacking breathing
- The color of the amniotic fluid is green.
- Green stains may appear on a baby's skin.
- Respiration that is laborious and rapid, with the amniotic fluid looking green.
- Birth immaturity
- Skin wrinkling
- Loss of weight
Diagnosis
- Baby's birth appearance.
- Inspection of the body.
- Analysis of blood gases.
- A chest x-ray.
Treatment
The baby's throat and nose are suctioned as soon as the head is delivered, and if the infant continues to appear sicker and experience breathing difficulties, the laryngoscope is used to continue suctioning meconium from beneath the vocal cords.
Other treatments includes:
- Move the infant to the special care area.
- In order to treat and prevent infection, use antibiotics.
- To maintain body temperature, keep the environment warm.
- Observe the vital signs.
- On a ventilator, keep an eye on the baby's health.
- apping the chest to break up a clot.
- By intravenous infusion, maintain nutrients and hydration levels.
- Place a nasogastric tube in and maintain zero oral intake.
- Keep the intake and outflow chart current.
Prevention
- Early maternal and fetal status monitoring and fast action.
- Encourage delivery in a hospital.
Nursing Consideration
- Evaluation of the fetus and newborn.
- Clearing of the airways and preservation of breathing
- Watch your body temperature and vital indicators.
- Follow the treatment plan.
- Therapy for the chest.
- If necessary, special treatment in a neonatal intensive care unit.
- Maintain nourishment by breastfeeding, express breast milk, and IV infusion.
- Keep an eye out for complications like fever, vomiting, seizures, and breathing problems.
- parental assistance
Complications
- Oxygen deprivation-induced brain damage
- Breathing difficulties
- Compromised lungs
- Infant with persistent pulmonary hypertension.
REFERENCE
Ahikari, R. K., & Krantz, M. E. (1997). Child nutrition and health (2nd ed.). Kathmandu: HLMC.
Chabers, A.M. (2007). Surgical nursing of children. India: Elsevier Private Limited.
Managing Newborn Problem: a guide for doctors, nurse, and midwives.
Potts, N., & Mandleco, B.L. (2007). Caring for children and their families (2nd ed.). India
Sharma, P.R. (2002). A handbook of pediatric problems. Kathmandu: HLMC
Shrestha, S., lohani, D., & Thakur, L, etal. (2000). Nursing care of children. Majahrajgunj Kathmandu: HLMC
Smeltzer, S.C., & Bare, B.B. (2004). Brunner Siddharth's, a textbook of medical surgical nursing (10th ed.). Lippincott: Williams and Wilkins.
Traumatic brain injury.com. 2001. <http://www.traumaticbraininjury.com/birth-trauma/meconium-aspiration-syndrome/>.
Tuitui, Roshani. Manual of Midwifery III. Kathmandu: Vidyarthi pustak Bhandar, 2014.
Wong, D.l., & Hockenberry, M.J. (1999). Nursing care of infants and children (7th ed.). London: Mosby.
Things to remember
- A infant with meconium aspiration syndrome breaths a mixture of amniotic fluid and meconium into the lungs shortly after delivery.
- Meconium is a type of feces that develops in a fetus's intestines prior to birth and has a dark green color.
- Your baby may develop MAS if they are under stress. When the fetus has less oxygen accessible to it, stress frequently results.
- A pregnancy that lasts past the due date (more than 40 weeks), a challenging or protracted labor, and certain maternal health conditions, such as hypertension (high blood pressure) or diabetes, are common causes of fetal stress.
- Breathing problems, a lack of breathing, a greenish tint of the amniotic fluid, weight loss, and limpness at birth are signs and symptoms of MAS.
- The baby's throat and nose are suctioned as soon as the head is born, and if the infant continues to appear unwell and experience breathing difficulties, the laryngoscope is used to continue suctioning meconium from beneath the vocal cords.
- Complications of MAS include collapsed lungs, respiratory issues, and brain damage brought on by a lack of oxygen.
Questions and Answers
What are the causes of MAS ?
Causes:
- Your baby may develop MAS if they are under stress. When the fetus has less oxygen accessible to it, stress frequently results. Fetal stress is frequently brought on by:
- An ongoing pregnancy after the due date (more than 40 weeks)
- Arduous or prolonged labor
- Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes or high blood pressure, that the mother had
- An ailment
- Mother with diabetes
- Pregnancy-related high blood pressure in the mother.
List the sign and symptoms of MAS ?
- Breathing problems
- Lacking breathing
- The color of the amniotic fluid is green.
- Green stains may appear on a baby's skin.
- Respiration that is laborious and rapid, with the amniotic fluid looking green.
- Birth immaturity
- Skin wrinkling
- Loss of weight
What are the treatment, nursing management and prevention of MAS ?
Treatment:
The baby's throat and nose are suctioned as soon as the head is delivered, and if the infant continues to appear sicker and experience breathing difficulties, the laryngoscope is used to continue suctioning meconium from beneath the vocal cords.
Additional therapies include:
- Move the infant to the special care area.
- In order to treat and prevent infection, use antibiotics.
- To maintain body temperature, keep the environment warm.
- Observe the vital signs.
- On a ventilator, keep an eye on the baby's health.
- Tapping the chest to break up a clot.
- By intravenous infusion, maintain nutrition and fluid levels.
- Place a nasogastric tube in and maintain zero oral intake.
- Keep the intake and output chart current.
Prevention:
- Early maternal and fetal condition monitoring and prompt action.
- Encourage delivery in a hospital.
Nursing consideration:
- Evaluation of the fetus and newborn.
- Clearing of the airways and preservation of breathing
- Watch your body temperature and vital indicators.
- Follow the treatment plan.
- Therapy for the chest.
- If necessary, special treatment in a neonatal intensive care unit.
- Maintain nourishment by breastfeeding, express breast milk, and IV infusion.
- Keep an eye out for complications like fever, vomiting, seizures, and breathing problems.
- Parental assistance
Define Meconium aspiration syndrome.
A newborn with meconium aspiration syndrome breathes a mixture of amniotic fluid and meconium into the lungs shortly after delivery.
© 2021 Saralmind. All Rights Reserved.

 Login with google
Login with google