Spinal Bifida
Subject: Child Health Nursing

Overview
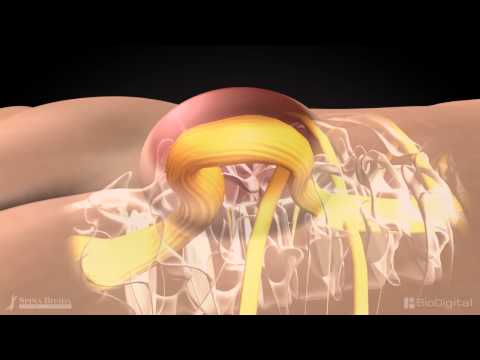
Spinal bifida is a bodily defect in the vertebral column through which the meningeal membrane and spinal cord may protrude or may not extend, leaving the defect buried and covered by skin. A disorder characterized by a spinal column developmental abnormality in which the arches of one or more spinal vertebrae fail to fuse. Spinal bifida, which literally means "cleft spine," is characterized by incomplete or defective brain, spinal cord, and meningeal development. The lumbar and sacral areas are the most commonly affected by the abnormality. Spinal bifida malformation is classified into two types: Spinal Bifida Occulta (hidden) and Spinal Bifida Cystic. The precise cause of spinal bifida is unknown. Scientists believe genetic, nutritional, and environmental variables are involved. Neural tube defects are caused by a teratogenic process that causes embryonic neural abnormalities to fail closure and differentiate abnormally. It happens between the 17th and 30th day of pregnancy. Swelling, a dimple in the skin, brain injury, paralysis, loss of sensation, blindness, convulsions, and other symptoms are common. Prompt surgery helps to prevent the additional nerve damage from infection and trauma but doesn’t restore normal function to the affected part of the spinal cord.
Spinal Bifida is a bodily defect in the vertebral column through which the meningeal membrane and spinal cord may protrude or may not extend, leaving the defect buried and covered by skin. A disorder characterized by a spinal column developmental abnormality in which the arches of one or more spinal vertebrae fail to fuse. Spinal bifida, which literally means "cleft spine," is characterized by incomplete or defective brain, spinal cord, and meningeal development. It is a neural tube defect, which is a form of birth defect. The lumbar and sacral areas are the most commonly affected by the malformation.
Types of the Spinal Bifida
Spinal bifida malformation falls into the categories, they are:
- Spinal Bifida Occulta (hidden)
- Spinal Bifida Cystic
- Meningocele
- Myelomeningocele/ Meningomyelocele
Spinal Bifida Occulta
Occulta is a Latin word that means "hidden," and it refers to the fact that a layer of skin hides the vertebral deformity or opening. This is the most frequent and mild kind of spinal bifida. The outer section of several vertebrae in occulta is not entirely closed. The spinal cord does not protrude because the openings in the vertebrae are so small. Visible signs of spinal bifida occulta, which can be visible in the newborn's skin above the spinal defect, include:
- An abnormal tuft or hair
- A collection of fat
- A small dimple or birthmark
Many people with this type of bifida do not even know thy have it, as the condition is asymptomatic in most cases.
Spinal Bifida Cystic
The disorder is known as "spinal bifida cystica" when the skin covering is faulty and a swelling is apparent above the spinal defect. It appears to be a sac-like structure that could be found anywhere in the lumbosacral area. It is protected by a thin membrane that is prone to leakage of CSF fluids.
-
Meningocele
The hernial protrusion of the meninges through the hole in the spine is known as meningocele. The vertebrae develop normally in this configuration, but the meninges are driven into the spaces between the vertebrae. Individuals with o meningocele are likely to face long-term health difficulties since the nerve system is unharmed. In this case, fluids flow from the spine and press against the skin. -
Myelomeningocele
Myelomeningocele is a severe form of spinal bifida that can lead to life-threatening problems. The meningeal membranes that surround the cord protrude through the defect or opening, generating a sac and causing significant neurological impairments. A portion of the spinal nerves protrude from the spinal canal, and nerves are frequently injured. It is the most frequent type of lesion that can occur anywhere along the midline of the back, but its most common location is in the lumbo- sacral portion of the spinal cord.
It is most common and significant form and leads to the disability in the affected individuals.
Causes of Spinal Bifida
- The precise cause of spinal bifida is unknown.
- Nobody understands what causes the neural tube to fail completely, resulting in a deformity.
- Scientists believe genetic, nutritional, and environmental variables are involved.
- Medications such as sodium valproate and insufficient folic acid ( vitamin)
Path Physiology
Neural tube defects are caused by a teratogenic process that causes embryonic neural abnormalities to fail closure and differentiate abnormally. It happens between the 17th and 30th day of pregnancy.
Risk Factors
- Race: Spinal bifida is more common in European.
- Sex: Girls are more affected.
- A family history of neural tube defect: Couples who have had one child with a neural tube defect have a slight chance have a higher chance of having another baby with same defects.
That risk increases if two previous children have been affected by the same condition.
- Folic acid deficiency: Folic acid (vitamins) and folate( vitamin B9) are very important for the healthy development and growth of the fetus. Lack of folic acid increases the risk of the spinal bifida and other neural tube defects.
- Medications: Anti-seizure medications like valproic acid(Depakene), seem to cause neural tube defects when taken during a period of pregnancy because they interfere with the body’s ability to use folate and folic acid.
- Diabetes: The risk of the spinal bifida increases with diabetes especially when the mother’s blood sugar is elevated early in her pregnancy have a higher risk of having a baby with spinal bifida.
- Obesity: There is a link between pre-pregnancy obesity and neural tube birth defects, including spinal bifida. Obese women may have more babies with spinal bifida possibly because they interfere with the body’s ability to use folic acid.
- Increased body temperature: Some evidence suggests that increased body temperature (hyperthermia) in the early months of pregnancy may increase the risk of spinal bifida.
Signs and Symptoms
- Swelling
- Dimple in skin
- Muscle weakness of the legs
- Brain damage
- Paralysis
- loss of sensation
- Seizures, especially if the child requires a shunt
- Blindness
- Fluid build up(hydrocephalus)
- Scoliosis(curved spine)
- Bowel and bladder control problems like urine incontinence, urinary tract infection
- Pressure sores
Diagnosis
-
Blood tests
- Second-trimester maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein (MSAF)
- Alpha- fetoprotein (AFP) is made naturally by the fetus and placenta
- But if abnormally high levels of this protein appear into mother’s blood stream it may indicate that the fetus has neural tube defects.
-
Ultrasound
-
An advanced ultrasound can also detect the signs of spinal bifida.
-
- Amniocentesis
- An analysis indicates the level of Alpha- fetoprotein(AFP) present in the amniotic fluid.
-
A small amount of alpha-fetoprotein is normally found in amniotic fluid when an open neural tube defect is present. The amniotic fluid contains an elevated amount of AFP.
- MRI
- CT- Scan
- X- Ray
Management
- Occult spinal bifida normally does not require treatment.
- Meningocele that did not affect the spinal cord necessitated surgery. In most cases, there is no paralysis.
- Meningomyelocele is usually operated on within 24-48 hours of delivery. Spinal cord release is a surgical procedure that substitutes the spinal cord.
- Prompt surgery helps to avoid further nerve damage caused by infection and trauma, but it does not restore normal function to the afflicted section of the spinal cord.
- To avoid pressure on a sac, place the infant in a prone position.
Other Management:
-
Pre-surgery
-
Maintain the baby's temperature by keeping him nil per orally. Cover the sac with a sterile dressing free of antiseptic solution and keep the baby prone or lateral.
-
-
Surgery
-
Surgical corrections within 24hours of birth for open lesion and within 48 hours for a closed lesion.
-
-
Indications of surgery
-
CSF should be sterile, no kyphosis or scoliosis, or o gross hydrocephalus and no other associated gross anomalies.
-
Nursing Management
-
Essential care of infants
- To avoid constipation, the baby should be fed properly, with enough of fluids and fiber-rich foods such as green vegetables, fruits, and whole grains.
- To avoid hypothermia, keep the baby's body temperature stable by dressing appropriately and keeping the environment temperature stable.
- To avoid cross infection, take care of the baby's chord and keep an open airway.
-
Infection prevention
- Keep the newborn in the right position to decrease the possibility of contamination from stool/urine.
- Always gently clean the faulty area with a sterile saline solution.
- Using sterile procedures, thoroughly clean the operative site.
- Prevent urethral infection with stool.
- Keep your perineum clean.
- Antibiotics should be given as a precaution.
-
Prevent lesion from trauma
- Handle the infant correctly by providing support in the affected area.
- Place the infant on his or her side.
- Apply a support and protective devices around the sac.
-
Supportive care
- Care for the bowel and bladder
- Keep the perineal area clean in terms of skincare.
- For a long time, avoid using wet diapers.
- Change the diapers on time.
- Take measurements of the infant's head circumference and fontanel, and look for evidence of rising intracranial pressure.
- Prevention of leg and hip abnormalities; newborns' passive range of motion, muscle stretching
- A baby's routine care before and after surgery.
- Proper rearing and weaning promotes the growth and development of the baby.
- Parents and other family members are encouraged to help with child care.
- Provide the proper technique and teach parents about routine baby care at home.
- Inform the family about the indicators of difficulty and go to the hospital right away.
- Encourage parents to help their infants based on developmental activities within the boundaries of their impairment.
- If the defect is not fixed, persuade the parent] to get a proper automobile for the lesion.
Things to remember
- Spinal bifida is a bodily defect in the vertebral column through which the meningeal membrane and spinal cord may protrude or may not extend, leaving the defect buried and covered by skin.
- A disorder characterized by a spinal column developmental abnormality in which the arches of one or more spinal vertebrae fail to fuse.
- Spinal bifida, which literally means "cleft spine," is characterized by incomplete or defective brain, spinal cord, and meningeal development.
- The lumbar and sacral areas are the most commonly affected by the abnormality.
- Neural tube effects
- are the outcome of a teratogenic process that causes embryonic neural abnormalities to fail to close and differentiate abnormally. It happens between the 17th and 30th day of pregnancy. The precise cause of spinal bifida is unknown.
- Swelling, a dimple in the skin, brain injury, paralysis, loss of sensation, blindness, convulsions, and other symptoms are common.
- Prompt surgery helps to avoid further nerve damage caused by infection and trauma, but it does not restore normal function to the afflicted section of the spinal cord.
- Occult spinal bifida usually does not require treatment, whereas meningocele, which does not involve the spinal cord, necessitates surgery. In most cases, there is no paralysis.
- Meningomyelocele usually operated at 24-48 hours after birth. Spinal cord release surgically replaces the spinal cord.
Questions and Answers
What do you mean by spinal bifida ?
- Specific to the body defect in the vertebral column where the meningeal membrane and spinal cord may or may not protrude such that the defect stays covered by skin, Spinal Bifida refers to this defect.
- A disorder when the arches of one or more spinal vertebrae fail to fuse. It is a developmental abnormality of the spinal column.
- The brain, spinal cord, and meninges grow improperly or incompletely in individuals with spinal bifida, which is a medical condition.
What are the types of spinal bifida ?
Types of the spinal Bifida
Spinal Bifida malformation falls into the categories, they are:
- Spinal Bifida Occulta:
- The Latin word occulta, which means "hidden," denotes that the abnormality or opening in the vertebrae is covered by a layer of skin. The most prevalent and mildest type of spinal Bifida is this one. Some of the vertebrae in occulta have some of their exterior portions open. The spinal cord does not protrude because the spaces between the vertebrae are so small. A newborn's skin may occasionally show visible signs of spinal Bifida occulta above the spinal deformity, such as:
- An unusual hair or tuft.
- An accumulation of fat.
- A little marking or dimple.
- Since this variety of Bifida is typically asymptomatic, many persons with it are unaware that they even have it.
- The Latin word occulta, which means "hidden," denotes that the abnormality or opening in the vertebrae is covered by a layer of skin. The most prevalent and mildest type of spinal Bifida is this one. Some of the vertebrae in occulta have some of their exterior portions open. The spinal cord does not protrude because the spaces between the vertebrae are so small. A newborn's skin may occasionally show visible signs of spinal Bifida occulta above the spinal deformity, such as:
- Spinal Bifida Cystic:
- The disorder is known as "spinal Bifida cystica" when the skin's protective layer is damaged and a swelling is seen over the spinal defect. It seems to be a sac-like structure that could be anywhere in the lumbosacral area. Cerebrospinal fluids may seep through the thin membrane that covers it because of its susceptibility to fear.
- Meningocele:
- The hernial protrusion of the meninges through the hole in the spine is known as a meningocele. In this version, the meninges are pushed into the spaces between the vertebrae but the vertebrae develop normally. As long as the neurological system is unharmed, people with meningocele are likely to have long-term health issues. The bodily fluids in this push against the skin when they leak out of the spine.
- Myelomeningocele:
- One of the most serious forms of spinal Bifida that can result in major consequences is myelomeningocele. Severe neurological impairments ensue from the meningeal membranes that surround the cord protruding through the hole or defect as well. The spinal nerves' protruding portions frequently cause nerve injury. Although it can occur anywhere along the midline of the back, the lumbo-sacral region of the spinal cord is where it most frequently occurs.
- It is the most prevalent and significant kind and causes handicap in those who are affected.
Write the causes and risk factors of Spinal Bifida ?
Causes of spinal Bifida:
- The precise cause of the spinal Bifida is yet unknown.
- Nobody is aware of what causes the neural tube to not completely close, resulting in a deformity.
- Scientists believe that environmental, nutritional, and genetic variables are involved.
- Medications such as sodium valproate and insufficient folic acid (vitamin).
Risk factors:
- Race:
- In Europeans, spinal bifida is more prevalent.
- Sex:
- More girls are impacted.
- A history of neural tube defects in the family:
- The likelihood of having another kid with the same problems increases somewhat for couples who have already had one child with a neural tube defect. If the same illness has previously impacted two children, the risk goes up.
- Folic acid deficiency:
- Folate, also known as vitamin B9, and folic acid are vital for the healthy growth and development of the fetus. The risk of spinal Bifida and other neural tube defects rises in the absence of folic acid.
- Medications :
- Because they prevent the body from using folate and folic acid, anti-seizure drugs like valproic acid (Depakene) appear to result in neural tube defects when taken during pregnancy.
- Diabetes:
- Diabetes raises the chance of spinal Bifida, particularly when the mother's blood sugar is increased early in her pregnancy, which increases the likelihood of having a baby with the condition.
- Obesity:
- Pre-pregnancy obesity has been linked to congenital abnormalities of the neural tube, including spinal Bifida. Because their bodies have a harder time using folic acid, obese mothers may give birth to more kids with spinal Bifida.
- Increased body temperature:
- Increased body temperature: According to certain research, hyperthermia during the first trimester of pregnancy may raise the chance of spinal Bifida.
What are the management and nursing management of spinal Bifida?
Management:
- Spinal Bifida occult usually does not require any treatment.
- Meningocele which does not involve the spinal cord required surgery. There is usually no paralysis.
- Meningomyelocele usually operated at 24-48 hours after birth. Spinal cord release surgically replaces the spinal cord.
- Prompt surgery helps to prevent the additional nerve damage from infection and trauma but doesn’t restore normal function to the affected part of the spinal cord.
- Place the infant in a prone position to avoid the pressures on a sac.
Other management:
- Pre-surgery:
- Keep the infant at a constant temperature and nil per ora. Keep the infant in a prone or lateral position and cover the sac with a sterile dressing devoid of any antiseptic solution.
- Surgery:
- Surgical adjustments should be performed within 48 hours for a closed lesion and within 24 hours for an open lesion.
- Indications of surgery:
- No kyphosis, scoliosis, gross hydrocephalus, or any concomitant gross malformations should be present in the CSF.
Nursing management:
- Essential care of infants:
- To avoid constipation, the baby should be fed properly and should receive lots of fluids and fiber-rich foods including green vegetables, fruits, and whole grains.
- To avoid hypothermia, the baby's body temperature should be maintained by appropriate clothes and a warm environment.
- In order to avoid cross infection, take care of the baby's cord and keep a clear airway.
- Infection prevention:
- To lessen the possibility of contamination from feces or urine, keep the baby in the appropriate position.
- Always gently wipe the affected region with a sterile saline solution.
- Use sterile approach to thoroughly clean the surgical location.
- Prevent stool from contaminating the urethra.
- Keep your perineum clean.
- Give the antibiotics as a preventative measure.
- Prevent lesion from trauma:
- Supporting in the damaged area will help you handle the baby properly.
- Baby should be placed in a side-lying position.
- Apply the protective coverings and a support to the sac.
- Supportive care:
- Bladder and bowel care.
- Maintain good skin care in the perineal area:
- Long-term use of moist diapers should be avoided.
- Timely diaper change.
- Take the infant's fontanel measurement and keep an eye out for any indicators of elevated intracranial pressure.
- Stretching newborns' muscles passively and performing passive range of motion exercises can help prevent leg and hip abnormalities.
- Regular care for a newborn before and after surgery.
- Correct weaning and raring help the baby's growth and development.
- Participation in child care is encouraged from parents and other family members.
- Give the right instruction and teach the parents how to take care of the infant at home on a regular basis.
- Visit the medical facility right away and alert the family to any complications.
- Encourage the parents to assist the infants in accordance with their developmental needs, allowing for any disabilities. Encourage the parent to take proper care of the injury if the flaw is not fixed.
© 2021 Saralmind. All Rights Reserved.


 Login with google
Login with google